In the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT), it is becoming increasingly important to establish a unified reference architecture and standardization system. In this paper, we will delve into the reference architecture of IoT, the main standards and their importance in practical applications to help readers better understand the design and realization of IoT systems.
1. Overview of the Internet of Things reference architecture
1.1 Definition and significance
The IoT Reference Architecture (IoT RA) is a conceptual framework that provides guidance for the design, deployment and operation of IoT systems. According to the latest ISO/IEC 30141:2024 standard, the IoT Reference Architecture aims to:
- Establishment of a harmonized terminology and conceptual framework
- Provide reusable design patterns
- Ensure interoperability between systems
- Promote the application of industry best practices
1.2 Main components
The IoT reference architecture contains three main core layers:
- perceptual layer
- Sensors & Actuators
- Data acquisition equipment
- Edge Computing Nodes
- network layer
- communication protocol
- Gateway equipment
- data transmission channel
- application layer (computing)
- Cloud Service Platform
- Data Processing Center
- user

2. Importance of IoT standardization
2.1 Interoperability Assurance
Standardization is essential to ensure that devices from different vendors can communicate and collaborate with each other. According to the latest statistics, standardization can:
- Reduces system integration costs by approximately 40%
- Improve equipment compatibility to 95% or more
- Reduction of development cycle time by an average of 30%
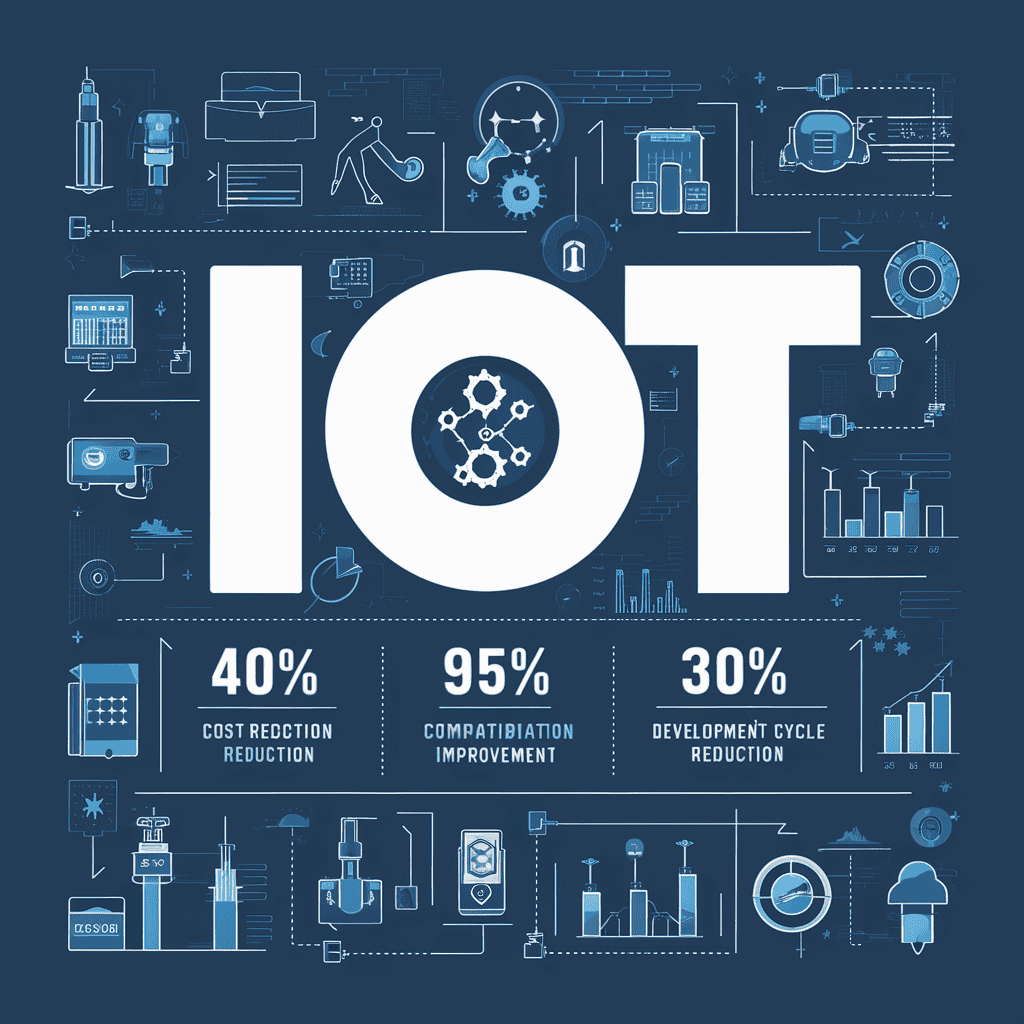
Figure 2: Analysis of benefits from IoT standardization
2.2 Data sharing and privacy protection
The standardized framework provides a uniform specification for data sharing while ensuring:
- Consistency of data formats
- Security of the transmission process
- Normative nature of privacy protection
3. Key IoT standards
3.1 ISO/IEC 30141
The latest version of ISO/IEC 30141:2024 provides updated IoT reference architecture standards, including:
- A unified conceptual model
- functional view
- Implementing Views
- Deployment View
3.2 OneM2M
OneM2M, a global IoT standardization organization, provides:
- Service level standardization
- interoperability specification
- security framework
3.3 OIC (Open Interconnect Consortium)
Provide open standards for interconnectivity:
- device discovery protocol
- Data Model Definition
- Secure authentication mechanisms
Figure 3: Comparison of major IoT standards
4. IoT architecture modeling practices
4.1 Example of Smart Home Architecture
Taking smart home as an example, modern smart home system adopts layered architecture to realize intelligent control and management:
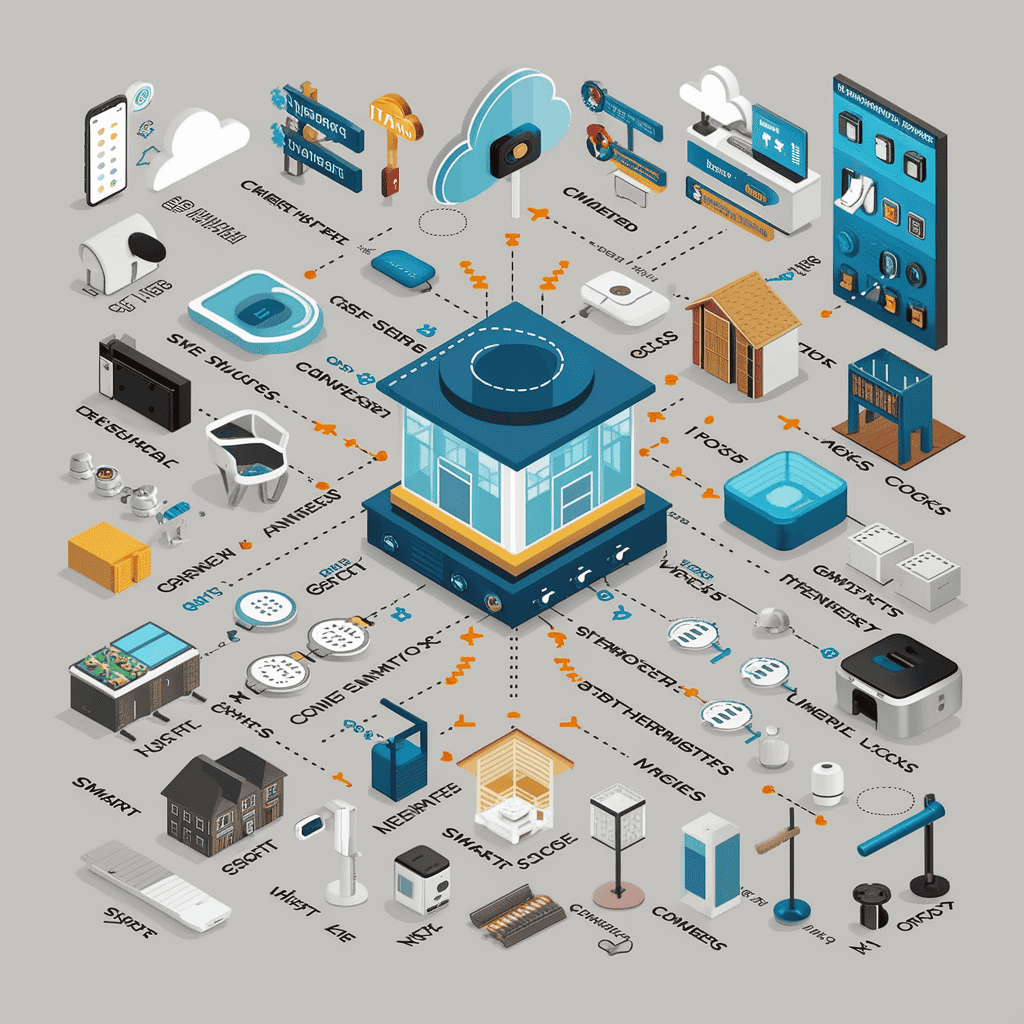
Figure 4: Schematic diagram of smart home system architecture
System Hierarchy Detail:
- Perception layer devices
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- intelligent lighting
- Security equipment
- Intelligent door locks
- Environmental monitors
- network layer implementation
- WiFi networks (2.4GHz/5GHz)
- Zigbee network
- Bluetooth network (BLE)
- Gateway equipment
- application layer function
- Mobile Application Control
- Intelligent Scene Linkage
- Data analysis services
- Remote monitoring and management
5. Case study: standardized smart home applications
5.1 Effectiveness of implementation
Data analysis of the effect of a smart home project after adopting a standardized architecture:
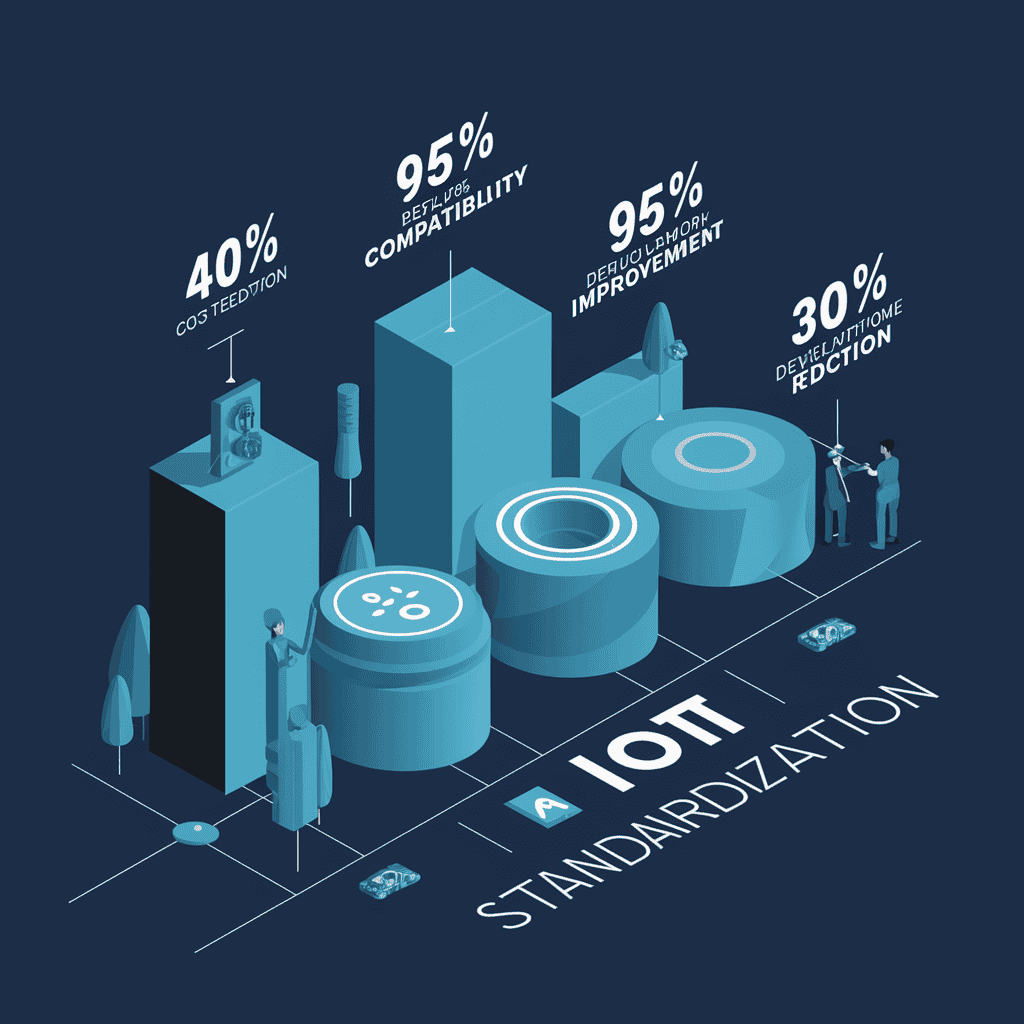
Figure 5: Comparison of effects before and after standardized implementation
5.2 Critical success factors
- UCP used
Adoption of standardized communication protocols to ensure seamless interconnectivity between devices
- Standardization of data models
Establishment of a unified data model to improve overall system efficiency
- Security framework implementation
Implementation of a complete security protection system to ensure the safety of user data
6. Future prospects
Future trends in IoT architecture and standardization:
- Evolution to Microservices Architecture
- More flexible service deployment
- Higher system scalability
- Enhanced edge computing capabilities
- Reduced network latency
- Enhancement of local processing capacity
- Improve the safety standard system
- Device authentication mechanisms
- Data Encryption Standard
- Privacy Framework
7. Extended reading
- In-depth analysis of the ISO/IEC 30141:2024 standard document
- OneM2M Technical Specification Details
- IoT Security White Paper Study
- Smart Home System Implementation Guide
8. References
- ISO/IEC 30141:2024 - Internet of Things Reference Architecture
- OneM2M Technical Specifications
- Open Interconnect Consortium Standards
- IoT Architecture Implementation Case Studies
内容审核:朱玉峰 Bread Zhu





