popularization of knowledge
[Indoor Positioning Technology] - Ultra Wide Band (UWB) Technology
发表于 知识科普 |Overview of positioning technology
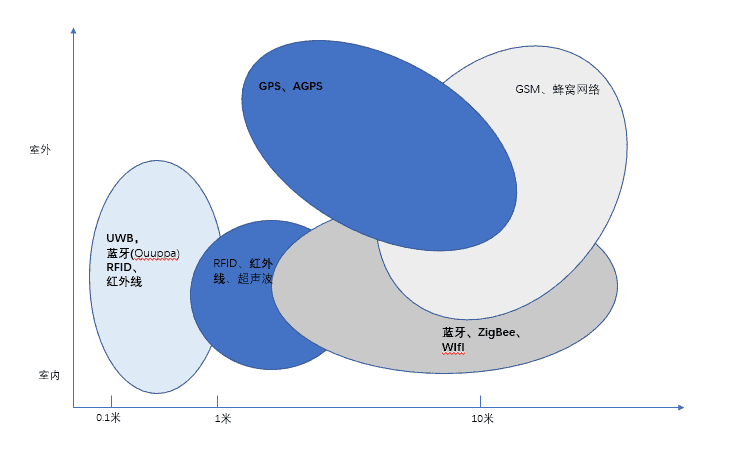
Positioning is a mechanism and system for determining the position of an object (including a person himself or other living things) in space; so far positioning technology has had global coverage with meter-level accuracy to workspace coverage with sub-millimeter-level accuracy, and has been used in a wide range of fields. From the coverage of planetary level positioning (can identify the position of each planet), global navigation satellite system positioning (the United States of America's GPS, Russia's GLONASS, Europe's Galileo, China's BeiDou, India's IRNSS), regional positioning (the military use more, similar to the United States of America's LORAN long-distance navigation system, which can cover 2,500 kilometers and the precision of the 30 kilometers) and local system positioning; of which the local system positioning; which has a meter-level precision global coverage to sub-millimeter precision workspace coverage, the application of a very wide range of fields. system) and local system positioning; of which local system positioning includes indoor positioning, workspace positioning and high performance in high-speed machine tools, laser scanning process. The branches of positioning technology broadly contain the following categories:
- Acoustic localization is the use of sound to determine the distance and direction of its source or reflector. Localization can be active or passive and can occur in gases (e.g., the atmosphere), liquids (e.g., water or grease) and solids (e.g., in soil or wood).
- TOF (Time of flight) technology: Distance is determined by measuring the propagation time of a pulsed signal between a transmitter and a receiver; when the distances to at least three positions are known, a fourth position can be determined using trilateration. The Global Positioning System (GPS) is an example.
- Space scanning systems use (optical) beacons and sensors; by aligning the sensors with the beacons, the angle between them can be measured. By triangulation, the position of an object can be determined
- The main advantage of inertial navigation positioning is that it does not require an external reference voltage source. Instead, it uses gyroscopes to measure rotation, or accelerometers to measure position relative to a known starting position and orientation. Since these systems measure relative rather than absolute position, they can suffer from cumulative errors and are therefore susceptible to drift. Periodic recalibration of the system will provide greater accuracy
- The phase difference system locates the phase shift of the input signal from the moving target transmitter versus the phase change of the input signal from the reference transmitter. This allows the relative motion of the transmitter with respect to the receiver to be calculated. As with inertial sensing systems, phase difference systems may suffer from cumulative errors and are therefore subject to drift, but because phase can be measured continuously, they are capable of generating high data rates
- Direct magnetic field sensing positioning uses a known magnetic field to derive direction or position: a simple compass uses the Earth's magnetic field to know its orientation in two directions. An inclinometer uses the Earth's gravitational field to know its orientation in the remaining third direction. The magnetic field used for orientation does not necessarily come from nature. A system of three electromagnets placed perpendicular to each other can define the space
- An optical positioning system is based on an optical element, such as a total station, which is an electronic/optical instrument used for surveying and building construction. It is an electronically transmitted latitude and longitude instrument with integrated electronic distance measurement (EDM) for measuring vertical and horizontal angles and slope distances from the instrument to specific points, as well as an on-board computer for collecting data and performing triangulation calculations
- Magnetic positioning exploits the typical magnetic field anomalies in indoor settings and uses them as unique place identification features. Magnetic sensor data from smartphones is used to wirelessly locate objects or people inside buildings. Magnetic positioning appears to be the most complete and cost-effective. It provides accuracy, has no hardware requirements, and has a relatively low total cost of ownership.GiPStechProprietary indoor positioning solution developed through intelligent integration of geomagnetic and inertial algorithms
- Hybrid positioning: Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages, so most systems use multiple techniques. Systems based on relative position changes (e.g., inertial systems) require periodic calibration against systems with absolute position measurements. Systems that combine two or more techniques are called hybrid positioning systems
Indoor positioning technology
Indoor positioning system (IPS) is a network of systems for locating people or objects where GPS, Beidou and other satellite technologies lack accuracy or fail completely, especially in multi-story buildings, shopping malls, train stations, airports, streets, parking lots, and underground locations; due to weak or absent signals from public networks it is difficult to implement relevant location information. or non-existent, it is difficult to implement relevant positioning information. While there are several successfully implemented systems in the industry, there is no universal standard for indoor positioning; instead, each installation is customized based on space dimensions, building materials, number of users, power consumption, accuracy needs, and budget constraints.
A wide variety of techniques and devices are used to provide indoor positioning, ranging from already deployed systems to reconfigured devices such as smartphones, WiFi and Bluetooth antennas, digital cameras, and clocks; to customized systems in which beacons are placed throughout customized and defined spaces. Light, radio waves, magnetic fields, acoustic signals and behavioral analysis are all used in indoor positioning system networks, for example, theVBOX's VIPS systemHigh positional accuracy can be achieved using UWB communication techniques; this accuracy is comparable to RTK-enabled GNSS receivers and can be achieved up to 2 cm outdoors. Indoor positioning systems use different techniques, including measurements to nearby anchor nodes (nodes with a known fixed position, e.g., WiFi / LiFi access points, Bluetooth beacons, or UWB Ultra Wideband beacons), magnetic localization, and navigational position derivation. They either actively locate mobile devices and tags or provide ambient location or environmental context for the device to be sensed. The characteristics of indoor positioning lead to design fragmentation, with systems utilizing a variety of optical, radio, and even acoustic technologies to accomplish the required design.
Virtually any wireless technology can be used for indoor positioning, and many different systems utilize the existing wireless infrastructure for indoor positioning; the accuracy of the positioning is dependent on the input and density of the equipment. The technologies for radio indoor positioning contain.ZigBee positioning,Lora Positioning,Bluetooth localization,Ultra-wideband UWB positioning,WIFI localization, please refer to the station documentation:What are the types of indoor positioning techniquesThe
UWB History
- 2002.WiMdia AllianceThe first UWB specification was introduced and the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allowed the license-free use of UWB systems for radar, public safety and data communications applications.
- 2005.By European Computer Manufacturers Association International (ECMA)Publication of ECMA-368 standard, high rate ultra-wideband PHY and MAC standard, multi-band orthogonal frequency division modulation (MB-OFDM) scheme
- 2007.IEEE 802.15.4a, evolved from OFDM to impulse radio (UWB IR)
- In 2012, the IEEE 802.15.4f standard was released, providing LRP UWB PHYs
- In 2015, IEEE 802.15.4-2015 defined 2 UWB PHYs, HRP Ch. 16 (802.15.4a/802.15.4-2011) and LRP Ch. 19 (802.15.4f-2012)
- 2017ETSI A working group, TGUWB, was established to focus on research and development of RF standards for short-range devices (SRDs), including short-range devices using UWB technology
- 2018.UWB AllianceEstablished to work on UWB global promotion and penetration, including RF spectrum and interoperability issues
- 2019.FiRa AllianceEstablished, based on IEEE 802.15.4/4z standard, enhanced UWB PHY & MAC
- 2020.IEEE 802.15.4zReleased, enhanced UWB PHY and associated ranging technology
UWB characteristics
UWB is a technology that transmits information over a wide bandwidth (>500 MHz). It allows the transmission of large amounts of signal energy, but does not interfere with the transmission of conventional narrowband and carrier signals in the same frequency band. Regulation in many countries allows for efficient utilization of radio bandwidth and enables high data rate Personal Area Network (PAN) wireless connectivity, longer range low data rate applications, and radar and imaging systems that coexist transparently with existing communication systems.
UWB (Ultra-wideband) was formerly known as pulse radio, but the FCC and the International Telecommunication Union's Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) now define UWB as antenna transmissions that transmit signals with a bandwidth of more than 500 MHz or a center frequency of 20%. Thus, pulse-based systems-where each transmit pulse occupies the UWB bandwidth (or an aggregation of narrowband carriers of at least 500 MHz; e.g., Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM))-can access the UWB spectrum based on rules.
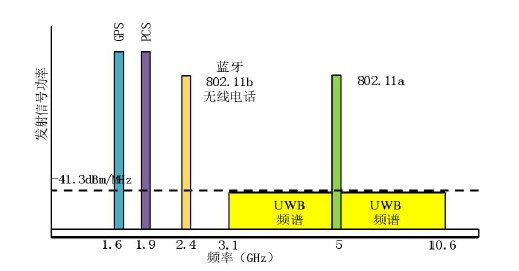
The significant difference between conventional radio transmission and UWB is that conventional systems transmit information by varying the power level, frequency and/or phase of a sine wave.UWB transmits information by generating radio energy at specific time intervals and occupying a large bandwidth, thus enabling pulse position or time modulation. It is also possible to modulate the information on the UWB signal (pulse) by encoding the polarity of the pulse, its amplitude and/or using quadrature pulses.UWB pulses can be sent occasionally at relatively low pulse rates to support time or position modulation, but can also be sent at rates up to the opposite of the UWB pulse bandwidth. Pulsed UWB systems have been demonstrated using a continuous stream of UWB pulses (continuous pulsed UWB or C-UWB) at channel pulse rates in excess of 1.3 billion pulses per second while supporting forward error correction coded data rates in excess of 675 Mbit/s
UWB Chip Suppliers
There are only a few chip suppliers in the world that can provide UWB chips in bulk, and some enterprises in mainland China have announced that they will launch related chips, such asChengdu Precision Technology,Beijing Qingyanxunke,Zhengzhou Lianrui Electronics,Guangzhou Hoyun Technology,All Tracks Technology,Nanjing Tangen Technology,Shanghai Huanxu Electronics,Shanghai Jen Microelectronics,Nanjing Wuxu,Hanwei Microelectronics,UWJ,Nurexium, a brand of mercury in neutrophil granulocytes, is a precious metal,Shenzhen Runan,Changsha Chuxin,Hangzhou Xinhua San; but most are modules, and chip-level products still haven't seen mass production in the market.
| provider | Product Model | (an official) standard | (radio) band | Release Date |
| Microchip | ATA8350 | LRP | 6.2-7.8 GHz | Feb 2021 |
| Microchip | ATA8352 | LRP | 6.2-8.3GHz | Feb 2021 |
| NXP | NCJ29D5 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Nov 12, 2019 |
| NXP | SR100T | HRP | 6-9 GHz | Sept 17, 2019 |
| Apple Inc. | U1 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Sept 11, 2019 |
| Qorvo | DW1000 | HRP | 3.5-6.5 GHz | Nov 7, 2013 |
| Qorvo | DW3000 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Jan 2019 |
| 3 dB | 3DB6830 | LRP | 6-8 GHz | |
| CEVA | RivieraWaves UWB | HRP | 3.1-10.6 GHz depending on radio | Jun 24, 2021 |
UWB positioning algorithms and techniques
Based on signal strength, RSSI (signal strength indicator)
When a wireless signal propagates in a specific channel, its signal strength obeys a certain attenuation model, so the RSSI localization algorithm calculates the distance between the mobile tag and the base station by measuring the field strength of the pulsed signal of the wireless signal and relying on the channel attenuation model. Since the sending node has the ability to communicate, RSSI is a low-power, low-cost ranging technology, the ideal environment, RSSI performance is very good characteristics; but indoor environments, shadow fading (from the signal transmission path on the obstacles) and multipath effect (electromagnetic wave propagation through different paths, each component field arrives at the receiving end of the time is different, according to their respective phases superimposed on each other to cause interference, making the original signal distortion) and other effects. The original signal is distorted) and other influences, will produce a large error
Based on the time of arrival, TOA (time of arriaal).
A localization scheme based on measuring the propagation time of electromagnetic waves, whose accuracy depends on two main points:
1. the degree of time synchronization between the base station and the tag;
2. Time resolution. The higher the degree of time synchronization and the higher the time resolution, the higher the positioning accuracy.
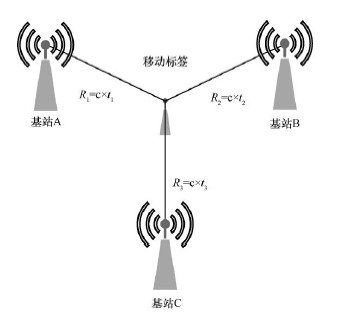
Based on time difference of arrival, TDOA (time difference of arrival)
Also known as the "hyperbolic positioning scheme", it is an improved version of the TOA positioning scheme. The tag sends out an electromagnetic wave signal, and the position of the tag is determined according to the time difference between this signal and different base stations. This scheme only needs to synchronize the time of the base station, which improves the feasibility, and it is a more widely used scheme in the current market.
Programs.

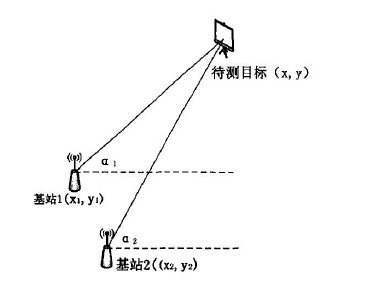
Based on the direction of arrival, DOA (direction of arriavl), can also be called: AOA (angle of arrival)
Angle-based AOA localization is the base station through the antenna array to measure the incident position of the wireless signal, which is used to calculate the angle between the tag and the base station, and finally triangulation method to derive the coordinates of the tag. However, this method has very high requirements for the direction and angle calculation of RF signals, especially the need to take a strong directional antenna or antenna array.
Time of flight method, TOF (TIME OF FLIGHT)
It is a bi-directional ranging technique that calculates distance by measuring the time of flight of a signal between the sender and receiver. The positioning method is essentially the same as TOA, except that the TOF positioning method does not require time synchronization between the devices, but the clock accuracy of the devices themselves will have an impact on the final result.
Common application scenarios for UWB localization
The main consumer advantage of indoor positioning is to extend location-aware mobile computing to indoor, involving an increasingly wide range of scenarios, these rely on the gradual reduction of the cost of the chip, more and more related module providers, and more and more extensive integration needs of the application class. The following are roughly some of the scenarios applications:
- Assistive features for the visually impairedThe visually impaired can be accurately located by UWB and then given audible instructions through background signals to ensure the safety of these people.
- Augmented Reality, virtual reality applications mainly used in gaming and commodity trading categories
- Location of people and assets within the campus; can be integrated with campus cards
- Museum-related navigation systems that allow visitors to be introduced to the products immediately after contact with them
- Shopping centers, including hypermarkets, provide customers with accurate location information
- Warehouse management, logistics management, precise location of materials and assets, especially the control of some dangerous goods
- Factory management of people and crates in the production line, by automatically tracking the progress of people or assets in the process and adding timestamps to them, such as tracking the waiting time for a toolbox or worker, the total time in the process, and in the production process, helps the process improvement work to make the process smoother and easier to improve the process
- Airports, bus stops, train stations and subway stations, where managers need to pinpoint the location for quick feedback; and also if it is bundled with a cell phone via UWB, then it can enable sensorless payment without the need to take out a cell phone to swipe the station's gates to gain access. Because it can be set in a very close range for identification.
- Location of parking lots, especially underground parking lots, where drivers can still find their vehicles in a timely manner
- Targeted advertising, because UWB can recognize the precise location at short distances, it is easy to achieve greater results for targeted advertising.
- Prison and correctional areas, for the supervision of inmates, if the inmates leave the area immediately alarm or give a warning
- Hospitals: Hospital medical equipment to ensure that it is in the right place or that it can be restored to its original condition in a timely manner after it has been used; and alarms or sirens to prevent children from being abducted when they leave the boundaries of a hospital birthing center.
- Hotels or restaurants, which can serve customers with precision
- Sports, the training of athletes need precise data indicators, through the UWB can be used to carry out precise calculations of the athletes' movement process, as a data base for improvement.
- Cruise ship: to protect the safety of tourists, there are some areas where tourists can not be allowed to enter, and once they enter the immediate alarm
- Indoor robots: robot vacuum cleaner, robot ironing;Robot toaster
- Tourism, in the process of tourism, often tourists can not keep up with the guide, the guide will count the number of people in each place, and if you give each tourist a label, the guide just refresh the signal received to know that the tourists are not in or not in progress
- Amusement parks; amusement park managers want to know what the foot traffic is near each show so they can focus on posting some information to do some triage.
- In-vehicle equipment: UWB technology interacts with the car to recognize when the user is approaching the car, assist in unlocking the doors, and control when to start the car, while making full use of UWB technology to achieve part of the radar detection function for foot radar, car personnel detection, etc., to open the trunk is more convenient, and the people in the car, especially infants and young children, is safer.
Related information
- IEEE, Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering: Is the drafter of the UWB standard 802.15.4.
- European Telecommunications Standardization Institute ETSI:: Primarily engaged in research and development of RF standards for short-range devices (SRDs)
- UWB Alliance: Established in December 2018 to enable UWB technology to become an open standard, working primarily on the transport and network layers
- FiRa Alliance: Established in 2019 with goals much like the UWB Alliance to promote interconnectivity and interoperability between individual products, i.e. interoperability
- APPLE's U1 chip
- Apple Watch Series 6 Features U1 Chip for Ultra Wideband
- NXP's UWB chip used in Xiaomi phone
- NXP:NCJ29D5: UWB IC for Automotive Applications
- iPhone 11's U1 Chip Uses 6Hz & 8GHz Frequencies In UWB Spectrum
- NXP Introduces UWB Chipset
SEIDEN Related Products
Content review.













