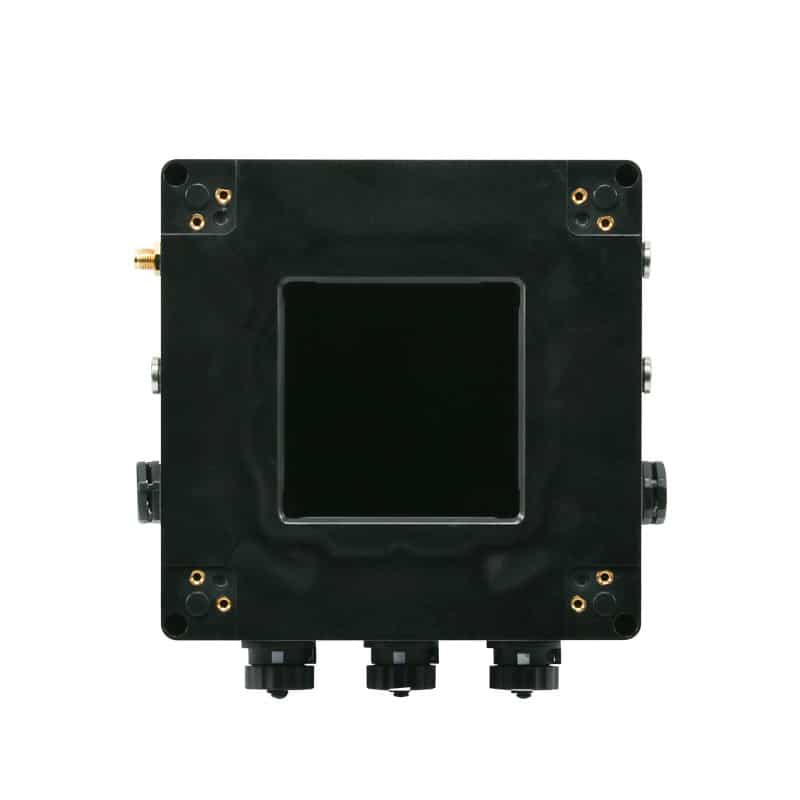
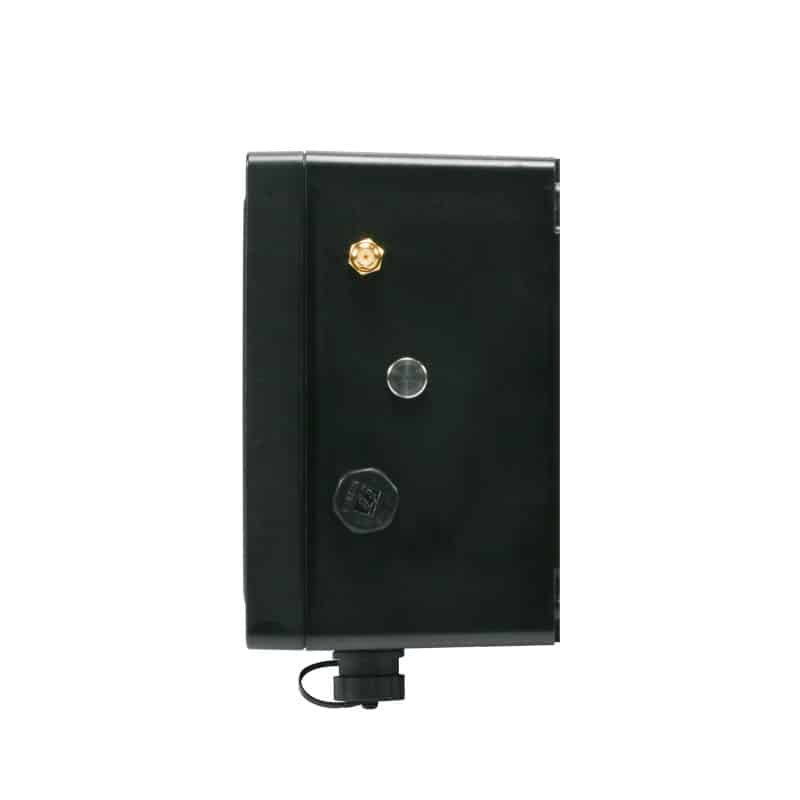
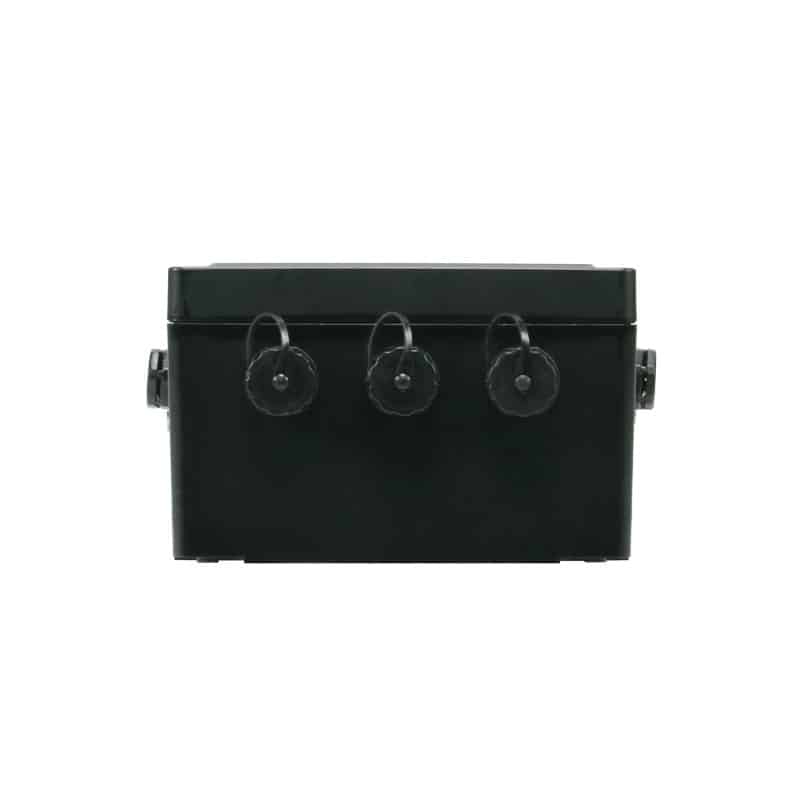
UWB high-precision vehicle-mounted WE-UG230
Product Features
- IEEE 802.15.4a UWB Wireless
- High power, line-of-sight transmission 1500 meters (@110Kbps)
- 485 interface
- Two independent relays (active, passive)
- Sub-G&BLE (optional)
¥3,219
WE-UG230 is Hainan Shidian Technology Co., Ltd. based on UWB positioning technology research and development of a vehicle positioning tags, support for IEEE802.15.4aUWB physical layer, support for 433MHz and BLE technology, mainly used for a variety of Internet of Things applications, more typical of vehicle tags man-vehicle collision avoidance and other applications. At the same time in the short-range increased short-range low-power assisted positioning technology.
Application Areas
Typical applications could be in-vehicle labeling, man-vehicle collision avoidance and other applications
interior positioningsummarize
In today's society, informationization, digitalization everywhere, wireless communication technology and navigation ranging technology has been very successful in various fields, all aspects of our lives can not be separated from the application of these technologies, for example, we go to a place to scan the nearby shopping malls, restaurants, and we are in the location of the formation of the cross-detection, but also for example, if you want to go to a public place during the recent outbreak of disease, not only do a good job of personal protection, wear a mask, but also need to go to scan the place to go to the QR code so that our relevant accounting quarantine information and trip information is refined and tied to the location we take. Personal protection, wear a good mask, but also need to go to scan the QR code of the place to go, so that our relevant accounting and quarantine information and trip information is refined and formed with the location of the place we take a binding relationship, which is equivalent to we have been to this place. Therefore, location service has become a very important part of our daily life.
With the increasing development of wireless sensor networks, the technical means on indoor positioning have all made rapid progress, especially theZIGBEE localization,WIFI localization,BLUETOOTH positioning,RFID positioning,UWB positioningIt has been widely used in the field of indoor positioning
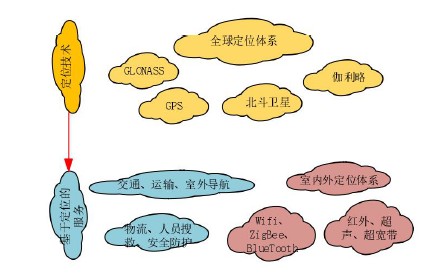
outdoor positioning techniques.global positioning system (GPS)(GPS) has been applied to every aspect of our life, especially we drive a car has been inseparable from the navigation, 20 years ago when I first arrived in Shanghai, I drive often in the passenger side will have a person to help me take the map to do the command in order to avoid going the wrong way, and now such a way of navigation was almost unimaginable at that time, our company agent of the Swiss brand UBLOX is the market of the module of this industry Pioneer, we will sell millions of module products every year to apply in various fields, especially since its launch in 2019 F9P this epoch-making product; because the accuracy of this product can reach the meter level, the price can be up to 1,000 yuan RMB or less, since the beginning of the introduction of a large number of customers have gained a large number of customers to seek and respond to the application of the field of automobiles, construction machinery, lawnmowers, drones, every year we are an agent of the number of shipments are very large. The number of shipments from one agent is very considerable, and we feel the huge potential of the positioning market. However, people still need to spend a large part of the time indoors to deal with positioning information, and the use of GPS in indoor environments will have many problems, the complexity of indoor environments is much higher than outdoor, satellite signals in indoor areas will face a variety of interferences, resulting in the signal reflected, refracted, or absorbed, so that it is not possible to use GPS indoors to carry out accurate positioning. And the demand for indoor positioning more and more, the demand for higher and higher precision; due to more and more large shopping malls, parking lots are also more and more large, and people expect to be able to find the required shopping malls or their own vehicles need the support of indoor positioning technology; large warehouses are often accompanied by the ERP, but sometimes the search for goods often need to be accurately located; and there are also some hazardous places, the need for accurate location of the equipment for the Processing, especially some security accidents rescue activities, the need for accurate location to plan routes to find trapped personnel or equipment; there are some intelligent workshop needs to detect the location of each device, in order to quickly and quickly do some processing; there are some confidential units, do not expect a certain type of people to enter, will be set up in some guarded areas, once a certain type of people close to or through the alarm will be alarmed; large-scale kindergartens or primary and secondary schools Children's safety control, unsafe places need to do some measures to ensure safe and controllable. So the application of indoor positioning technology will be imperative!
The most widely used methods for location information
Based on signal strength, RSSI (signal strength indicator)
When a wireless signal propagates in a specific channel, its signal strength obeys a certain attenuation model, so the RSSI localization algorithm calculates the distance between the mobile tag and the base station by measuring the field strength of the pulsed signal of the wireless signal and relying on the channel attenuation model. Since the sending node has the ability to communicate, RSSI is a low-power, low-cost ranging technology, the ideal environment, RSSI performance is very good characteristics; but indoor environments, shadow fading (from the signal transmission path on the obstacles) and multipath effect (electromagnetic wave propagation through different paths, each component field arrives at the receiving end of the time is different, according to their respective phases superimposed on each other to cause interference, making the original signal distortion) and other effects. The original signal is distorted) and other influences, will produce a large error
Based on the time of arrival, TOA (time of arriaal).
(1) A localization scheme based on measuring the propagation time of electromagnetic waves, the accuracy of which depends on two main points: 1,
The degree of time synchronization between the base station and the tag; 2. Time resolution. The higher the degree of time synchronization,
The higher the time resolution, the higher the positioning accuracy.

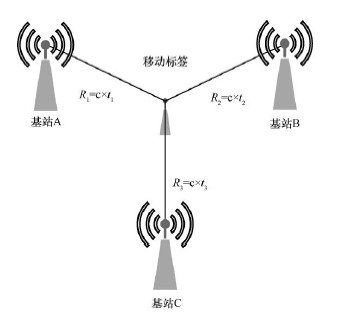
Based on time difference of arrival, TDOA (time difference of arrival)
Also known as the "Hyperbolic Positioning Scheme", it is an improved version of the TOA Positioning Scheme. The tag emits electromagnetic waves
signal, the location of the tag is determined based on the time difference of this signal to different base stations. The program only
The need to synchronize the time of the base station improves the feasibility, and it is a more widely used in the market today.
Programs.
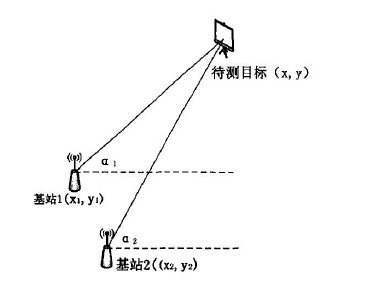
Based on the direction of arrival, DOA (direction of arriavl), can also be called: AOA (angle of arrival)
Angle-based AOA localization is the base station through the antenna array to measure the incident position of the wireless signal, which is used to calculate the angle between the tag and the base station, and finally triangulation method to derive the coordinates of the tag. However, this method has very high requirements for the direction and angle calculation of RF signals, especially the need to take a strong directional antenna or antenna array.
Time of flight method, TOF (time of flight)
It is a bi-directional ranging technique that measures the time of flight of a signal between the sender and the receiver by
to calculate the distance. Its localization method is essentially the same as TOA, except that the TOF localization method does not
Time synchronization between devices is required, but the clock accuracy of the devices themselves can have a significant impact on the final result.
implications
UWB positioning technology
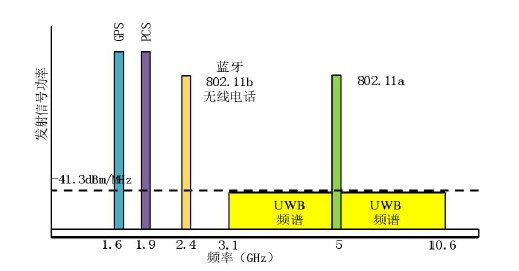
UWB technology is a wireless carrier communication technology that utilizes sinusoidal narrow pulses of nanoseconds or micro-nanoseconds for data transmission. It first originated in the 1960's, utilizing ultrashort baseband pulses for communication and used for radar detection in the military; in the 1990's, according to the FCC's definition of UWB, it has the following main characteristics: absolute bandwidth is greater than 500 MHZ or relative bandwidth is greater than 20%, signal bandwidth in 3.1-10.6GHZ, and the center frequency is greater than 2.5GHZ. maximum transmit power does not exceed -41.3dBm/MHz.
In terms of spectrum, ultra-wideband differs from narrowband and broadband in that it has a wider frequency band.
| Signal Type | Signal bandwidth/center frequency |
|---|---|
| narrowband | Relative bandwidth ≤1% |
| wideband | 1%≤Relative Bandwidth≤25% |
| Ultra Wideband (UWB) | Relative bandwidth >25% or center frequency >2.5GHZ |
| positioning technology | anti-interference | positioning accuracy | effective distance | penetrating | Problems and limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WIFI | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | 3-5 meters | 30 meters | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | Poor signal stability |
| Bluetooth | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | 2-3 meters | 10 meters | center | Communication distance, requiring large deployment of base stations |
| Zigbee | vigorous | 1 meter | 30 meters | vigorous | Short communication distance and low precision |
| RFID | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | 10 cm | 30 meters | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | Easily disturbed, poor privacy |
| UWB | vigorous | 10 cm | 200 meters | vigorous | High hardware costs |
| infrared ray | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | 5-10 meters | 10 meters | (following a decimal or fraction) slightly less than | Straight line of sight, easy to interfere |
The signal characteristics of UWB are mainly: nanosecond time accuracy, wider frequency band, low transmit power, carrierless baseband transmission. Due to the limited transmit power of UWB, its transmission distance is also subject to many limitations in the civilian short-range wireless technologies are IEEE802.11a, Bluetooth, HomeRF, compared as follows

Common TDOA algorithms
- Fang algorithm: for positioning, it is simple to solve the hyperbolic equations, linearize the non-linear equations, and then minimize the error of the equations to arrive at the estimated position of the target to be located, this method is only applicable to indoor 2D positioning
- Least square (LS) localization algorithm: simple and fast, not an optimal solution
- Weighted Least Squares (WLS) Localization Algorithm
- Chan's Positioning Algorithm: Positioning accuracy is better when the measurement accuracy is high, but when the anchor position deviates or the measurement accuracy is general, the positioning performance decreases faster.
- CTK (Chan-Taylor-Kalman) localization algorithm; using Chan's algorithm to obtain the initial coordinates of the localization tags, and use this as the initial point of Taylor's algorithm iteration to get more accurate localization results, and finally use the improved Kalman to eliminate the abnormal data caused by the non-visual distance, multipath and other environments in the process of the experiment, so that the localization is more accurate.
- The localization algorithm of Taylor's series expansion requires iterative operations with initial values close to the actual position, otherwise convergence is slow and even localization is not possible due to poor choice of initial values
Error factors in UWB localization systems
- Antenna delay error: Transmit and receive delays originating from within the chip
- Clock error: due to process, working environment and other issues, different devices have a certain clock frequency does not
- Consistency issues: For positioning methods such as TOA, TDOA, etc., the clock synchronization process can also have some errors
- Multipath Error: In addition to receiving the normal signal, the receiving end also contains the signal through reflection, refraction brought about by error
specification
| sports event | descriptive | |
| summarize | ||
| Diethylammonium chloride | WE-UG230 | |
| Relevant norms | IEEE 802.15.4a | |
| IEEE 802.15.1 | ||
| connector | Airline plug (left) | Power Supply, RS485 |
| Airline plug (right) | Active Relay, Passive Relay | |
| Input Voltage | DC 12 ~48V | |
| power wastage | <5 W | |
| Ranging Refresh Rate | 0.1~20Hz (adjustable) | |
| Radio Frequency Specifications (UWB) | ||
| operating frequency | 3.25 GHz~3.74 GHz (channel1) | |
| 3.77 GHz ~ 4.24 GHz (channel 2) | ||
| 6.24GHz~6.74GHz (channel5) | ||
| physical velocity | 110 Kbps | |
| 850 Kbps | ||
| 6.8 Mbps | ||
| Output power (25℃) | -41dBm/MHz (typical), -13dBm/MHz (maximum) | |
| channel bandwidth | 500MHz | |
| Antenna Gain | 1dBi | |
| RF Specifications (BLE)optional) | ||
| Job Channel | 2400MHz ~2483.5MHz | |
| physical velocity | 500Kbps | |
| 1Mbps | ||
| 2Mbps | ||
| output power | 4dBm | |
| Antenna Gain | 2dBi | |
| RF Specifications (Sub-G Option) | ||
| operating frequency | 470-510MHz | |
| physical velocity | 110Kbps | |
| channel bandwidth | 850KHz | |
| output power | 17 dBm (Max) | |
| Antenna Gain | 2 dBi | |
| Software Specifications | ||
| UWB operating mode | In-vehicle labeling | |
| Corner Labeling | ||
| Configuration | CLI, software configuration tools | |
| Relay Specifications | ||
| Operating Voltage/Circuit | 250V @5A Max | |
| response time | Maximum 1 second | |
| Physical Specifications | |
| Dimensions (mm) | 125 x 125 x 80 |
| Weight (g) | 600 (excluding lugs, antennas) |
| Environmental specifications | |
| temp | Working Temperature: -20℃~65℃ |
| Storage temperature: -40ºC to 85ºC | |
| humidity level | Operating humidity: 0% to 90% without condensation |
| protection class | IP65 |
| RoHs | compatibility |
Interface Description
WE-UG230 external lead two aviation plug line, the left side of the aviation plug line for the DC power line (DC interface), 485 data line (configuration interface), the left side of the aviation plug line power line, the role of the WE-UG230 power supply, the internal sequence of red for the power supply +, black for the power supply -, the standard configuration for the DC interface, the configuration of the interface in the form of a RJ45 485 connector, the internal sequence of blue and white 485A, green and white 485B, green for the GND. The internal wire sequence of blue and white is 485A, green and white is 485B, and green is GND.
The first relay line of the right aviation plug line is an active relay connector, the wire sequence description defaults that D0 and GND have voltage output, D1 and GND have no voltage output; after the equipment is powered on, D0 and GND have no voltage output, D1 and GND have voltage output. The second line of the right navigation plug line is a passive relay connector, and the wire sequence description defaults that D0 and GND are connected and D1 and GND are disconnected; after the relay works, D0 and GND are disconnected and D1 and GND are connected.

Models and accessories
| name (of a thing) | Specification | quantities | part numbers |
| WE-TG230 | In-vehicle labeling | 1 | AA01UG230P00 |
| power cable (of an appliance etc) | One-part-two-way plug to DC and RJ45 power cord | 1 | / |
| relay line | One copy of 2hang plug to 3.81 3P relay adapter wire | 1 | |
| UWB antenna | 1 |
Annexes (not included in the scope of delivery, please contact Fombaux business in advance if required)
| name (of a thing) | Specification | part numbers |
| power adapter | 12V, 1.5A Power Adapter, Black | AD0201120000 |
This product cannot be used alone, it needs to be used with our card reader and handhelds.
maybeContactsThe sales staff of the company will give you reference advice:
Resource support
Case Sharing





























