summarize
In today's society, informationization, digitalization everywhere, wireless communication technology and navigation ranging technology has been very successful in various fields, all aspects of our lives can not be separated from the application of these technologies, for example, we go to a place to scan the nearby shopping malls, restaurants, and we are in the location of the formation of the cross-detection, but also for example, if you want to go to a public place during the recent outbreak of disease, not only do a good job of personal protection, wear a mask, but also need to go to scan the place to go to the QR code so that our relevant accounting quarantine information and trip information is refined and tied to the location we take. Personal protection, wear a good mask, but also need to go to scan the QR code of the place to go, so that our relevant accounting and quarantine information and trip information is refined and formed with the location of the place we take a binding relationship, which is equivalent to we have been to this place. Therefore, location service has become a very important part of our daily life.
in the wake ofwireless sensorThe increasing development of the network, about the indoor positioning of the technical means have also made rapid progress, especially theZigBee positioning,WIFI localization,BLUETOOTH positioning,RFID positioning,UWB positioningIt has been widely used in the field of indoor positioning.
Positioning methods
The data from the front-end of all positioning technologies will be used to obtain various signals through various communication methods; however, they are all based on the following common principles
Proximity perception mode
Through the reception of radio frequency signals to determine whether the mobile device is close to the base station; similar to our time and attendance system, the implementation of this approach is relatively simple, but the positioning accuracy will be relatively low
triangulation (math.)
This approach is based on the coordinates of the plane, is in the acquisition of the target to be measured relative to the angle of the two known reference points combined with the distance information between the two reference points can determine the unique triangle, you can determine the position of the target to be measured.
center of gravity (math.)
It is to calculate the center-of-mass coordinates as the coordinates of the mobile device based on the positions of all known beacons (beacons) within the receivable signal range of the mobile device. Correspondingly, the weight of the corresponding beacon can also be set according to the received signal strength indication, and the weighted center of mass is obtained as the coordinates of the mobile device. The algorithm of this method is easy to understand, the computation amount is small, and the positioning accuracy depends on the density of beacons.
Multilateral positioning method
It is to determine the position of the target to be measured by measuring the distance between the target to be measured and a known reference point. Multiple distance estimation methods can be used in a multilateral positioning based localization system, the
(math.) pole method
The position of a point to be measured is determined by measuring the distance and angle relative to a known reference point. This method requires only the positional coordinates of a known reference point and is therefore very easy to use and has been widely used in geodesy.
fingerprintprinting
A fingerprint database is established in the localization space, and localization is achieved by comparing the actual information with the parameters in the database. The advantage of fingerprint localization is that there is almost no need for reference measurement points, and the localization accuracy is relatively high; however, the disadvantage is that the workload of building the fingerprint database offline in the early stage is huge, and at the same time, it is difficult to be adaptive to the scene with large environmental changes
air position projection method
It is based on the known previous position, the current position is obtained by calculation or known movement speed and time calculation. The data is stable and non-dependent, but the method suffers from cumulative error, and the positioning accuracy deteriorates with increasing time
localization algorithm
Time of Arrival (ToA) / Time of Flight (ToF)
ToA refers to distance measurement using the time of signal propagation. It should be noted that electromagnetic waves propagate at different speeds in different media, usually inversely proportional.ToA depends on the accuracy of the time. Since the multipath problem is currently difficult to apply in indoor localization (autocorrelation peaks in the signal referenced to the LoS beam may not be resolved), the application of wider frequency bands may be considered to solve this problem
Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA, Time Difference of Arrival)
The position of the receiver is calculated using the difference in arrival time of a synchronized transmitter with a known position. TDOA is a method of positioning using time differences, whereby the distance of the signal source can be determined by measuring the time it takes for the signal to arrive at the monitoring station. Using the distance from the signal source to multiple radio monitoring stations (with the radio monitoring station as the center and the distance as a radius for a circle), the position of the signal can be determined. By comparing the time difference of the signal arriving at multiple monitoring stations, a hyperbola can be made with the monitoring station as the focus and the distance difference as the long axis, and the intersection of the hyperbolas is the position of the signal.TDOA is a multi-site-based positioning system, so at least three or more monitoring stations must be available for simultaneous measurements for the positioning of the signal. Each monitoring station is relatively simple and consists of a receiver, an antenna and a time synchronization module.
Round Trip Time (RTT) / Roundtrip
The RTT determines the location of the terminal by measuring the downlink PRS, and the uplink SRS separately to obtain the RTT of the located terminal with multiple base stations. This localization method supports both single-station and multi-station localization. When only one base station is involved in the positioning, RTT needs to be combined with AoA. RTT does not require strict synchronization between stations and can be used both indoors and outdoors.
Phase of Arrival (PoA) / Phase Difference (PD).
PoA uses the phase of the received carrier to determine the distance between two devices. To mitigate phase wrap, the phase of the received signal is evaluated at multiple frequencies. The distance is determined by the phase transition rate.
Doppler Ranging
The Doppler ranging technique is used to observe the relative speed between the transmitter and receiver. If a stationary source is used, the absolute velocity along the line of sight can be derived from the measured Doppler frequency shift. Given a known initial position and multiple Doppler frequency observations, the displacement of a mobile device can be determined
Angle of Arrival (AoA) / Angulation / Triangulation / Direction based Positioning:
AOA (Angle of Arrival) positioning is a two-base station positioning method based on the angle of incidence of the signal. The positioning algorithm based on the angle of arrival of the signal is a typical ranging-based positioning algorithm, in which the direction of arrival of the signal from the transmitting node is sensed by some hardware device, and the relative bearing or angle between the receiving node and the anchor node is calculated, and then the position of the unknown node is calculated using triangulation or other means
Near-Field Electromagnetic Ranging (NFER).
NEER is based on the principle that the phase of the electromagnetic field varies with the distance around the antenna, NFER has a potential range of distance measurement accuracy from 30 cm to 1 meter, with an operating range of up to 300 meters
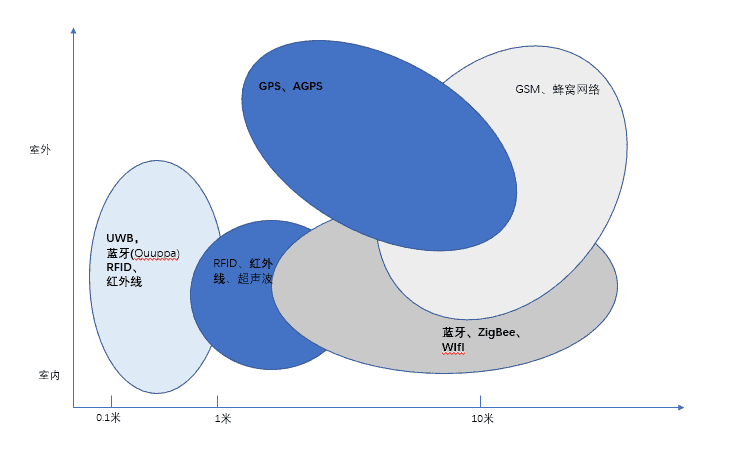
Several common indoor positioning techniques
Various positioning technologies have different focuses and involve different fields and markets. In specific scenarios, it is necessary to consider various aspects to decide to use that kind of program to carry out, the general practical considerations are positioning accuracy, positioning range, the number of positioning, the number of users, privacy, equipment installation, update frequency, power consumption, scalability, compatibility with other systems, the format of the output data, and most importantly, the cost. Therefore, it can be said that there is no single technology in this field that can be used in all scenarios and fields; it can only make some trade-offs and judgments according to the specific scenarios and needs.
Zigbee positioning
ZigBee is a short-range, low-rate wireless networking technology that falls between RFID and Bluetooth. It has its own radio standard, where thousands of tiny sensors communicate with each other in a coordinated manner to achieve localization. These sensors require very little energy to relay data from one sensor to another through radio waves, so their communication efficiency is very high.ZigBee's most notable technical features are its low power consumption and low cost. Our company agent digi has a strong lead in ZigBee related technology.
WI-FI localization
WiFi has been widely deployed in public places in the city such as large supermarkets and shopping malls, schools, and enterprises, etc. WiFi indoor positioning technology has seen many representative research results, such as indoor positioning systems such as the RADAR system, the Nibble system, and the Weyes system. Due to the popularity of WiFi network, WiFi positioning is a popular positioning technology, which can be popularized and promoted due to its accuracy of meters, low positioning cost, large range of sending and receiving positioning signals, and high applicability. However, whether it is used for indoor or outdoor positioning, Wi-Fi transceiver can only cover an area within a radius of 90 meters, and it is easy to be interfered by other signals, which affects its accuracy, and the energy consumption of the locator is also high.Skyhookis a company that specializes in WIFI location algorithms and operates the world's largest independent location network, consisting of more than 4.5 billion geo-located Wi-Fi hotspots and more than 180 million geo-located cell IDs. Now acquired by Qualcomm
Bluetooth Positioning
Most of the Bluetooth technology is used for indoor positioning by measuring the signal strength; iBeacon is a protocol technology formulated by Apple dedicated to Bluetooth positioning, with a positioning accuracy of 2~3m. Quuppa's Bluetooth positioning products, which are represented by our company, are based on the low-power Bluetooth® technology, with a unique method of arriving at the angle of the signal, and a positioning accuracy of up to 10cm can be achieved. For details, please refer to our store information and Quuppa's website.
RFID positioning
Radio Frequency Identification (Radio FrequencyIdentification, referred to as RFID) positioning technology using radio frequency signals for non-contact two-way communication exchange of data for the purpose of identification and positioning; this technology has a short role in the distance, generally up to tens of meters. Can be obtained within a few milliseconds centimeter-level positioning accuracy information, and the transmission range is very large, low cost; but because of its radio frequency signal does not have the ability to communicate, only the use of radio frequency identification technology can not be indoor positioning, must be combined with other auxiliary technology to complete.
UWB positioning
Ultra WideBand (UWB) technology does not require the use of carriers in conventional communication systems, but instead transmits data by sending and receiving very narrow pulses with nanosecond or sub-nanosecond bandwidths, resulting in bandwidths on the order of GHz for indoor positioning. Ultra-wideband can be used for precise indoor localization, such as position discovery of soldiers on the battlefield and robot motion tracking. Compared with the traditional narrowband system, the ultra-wideband system has the advantages of strong penetration, low power consumption, good multipath resistance, high security, low system complexity, and can provide precise positioning accuracy. Therefore, ultra-wideband technology can be applied to indoor stationary or moving objects and human positioning tracking and navigation, and can provide very accurate positioning accuracy.The main supplier of UWB positioning chips is Decawave; in 2020 it was acquired by Qorvo for $400 million.
UWB Chip Suppliers
| provider | Product Model | (an official) standard | (radio) band | Release Date |
| Microchip | ATA8350 | LRP | 6.2-7.8 GHz | Feb 2021 |
| Microchip | ATA8352 | LRP | 6.2-8.3GHz | Feb 2021 |
| NXP | NCJ29D5 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Nov 12, 2019 |
| NXP | SR100T | HRP | 6-9 GHz | Sept 17, 2019 |
| Apple Inc. | U1 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Sept 11, 2019 |
| Qorvo | DW1000 | HRP | 3.5-6.5 GHz | Nov 7, 2013 |
| Qorvo | DW3000 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Jan 2019 |
| 3 dB | 3DB6830 | LRP | 6-8 GHz | |
| CEVA | RivieraWaves UWB | HRP | 3.1-10.6 GHz depending on radio | Jun 24, 2021 |
infrared positioning
infrared positioningPositioning is carried out through specific infrared rays (InfraredRay) emitted by infrared emitters received by indoor optical sensors.Active BadgeSystem, an infrared outdoor positioning system developed by AT&T Labs at the University of Cambridge, is known as the first-generation indoor positioning system; Ambiplex proposed the IR.Loc system in 2011, which measures thermal radiation for positioning. Loc system measures thermal radiation for localization, and its positioning accuracy reaches 20~30 cm within 10 m. Infrared indoor positioning accuracy is relatively high, but it can't penetrate obstacles, and only propagates within the straight line visible distance, with a shorter effective distance, which is greatly affected by the indoor layout and lighting, and the positioning cost is higher.
A-GPS positioning
A-GPS(Assistant-GPS, Assisted Global Positioning Technology) was proposed by Qualcomm in the U.S.A. It utilizes cell phone base station signals, supplemented by connecting to a remote server, with a receiver to achieve fast positioning, and is widely used in GPS-enabled cell phones.A-GPS positioning is fast and accurate, but it takes up a lot of communication resources because it has to communicate with the server over a number of networks. UBLOX, as a Switzerland-based supplier of positioning and wireless communication technologies for the automotive, industrial and consumer markets, is one of the world's top-ranked GPS suppliers. The accuracy of its consumer F9P module can already reach the meter level.
ultrasonic positioning
ultrasound (scan)Ranging is mainly used to reflective ranging method, through the triangulation and other algorithms to determine the location of the object, that is, transmit ultrasonic waves and receive the echo generated by the object to be measured, according to the time difference between the echo and the transmitted wave to calculate the distance to be measured, and in some cases, one-way ranging method is used. Ultrasonic positioning overall positioning accuracy is high, simple structure, but ultrasonic by the multipath effect and non-line-of-sight propagation is greatly influenced by the need for a large number of underlying hardware facilities investment, the cost is too high!
Inertial Sensor Positioning
The motion data collected by inertial sensors, such as acceleration sensors, gyroscopes, etc., are used to measure the speed, direction, acceleration and other information of the object, and the position information of the object is obtained through various operations by the integral localization method or based on the navigational position speculation method. The object or task movement or walking time growth, inertial navigation data error is also accumulating. Therefore, this technology is generally combined with GNSS technology for auxiliary navigation, and is used as an auxiliary positioning when other effective positioning signals cannot be received.
reference data
Mautz R. Indoor Positioning Technologies
China Mobile 5G High Precision Positioning Capabilities White Paper.pdf
Content Reviewer: Josh Xu





