summarize
Sound noise sensors (sound sensor or acoustic sensor) also belong to the manyIoT SensorsOf a class, we talked about the temperature sensing, humidity sensing, light sensing and other sensors of the physical environment we are in, sound and noise is also such a class, in addition to the noise we can feel the comfort of the environment outside, we can listen to some of the machine's sound and noise as a means of determining the working status of the machine, whether it is necessary to start overhauling or maintenance.
The sound sensor consists of a built-in condenser microphone, a height detector and an amplifier that is very sensitive to sound. The microphone score converts the sound signal into a digital signal that can be read. They usually have a small magnet diaphragm product surrounded by a twisted wire. Sound waves cause the diaphragm to vibrate, which in turn causes the magnet to vibrate and generate an electric current inside the coil. The most commonly used microphones in our lives are moving coil, aluminum ribbon or condenser microphones.
The sound sensors market has been categorized into low frequency detection (20,000 Hz); high frequency detection sound sensors can detect sound waves with frequencies above 20 kHz. These are often referred to as ultrasonic or ultrasonic sensors. These sensors are mostly used in several areas such as automotive, fitness care, business, purchasing electronics as well as protection and surveillance. These can be used in applications including robotic sensing, can sizing, item detection, cycle management and parking assistance systems, ADAS systems, self-driving car systems, business automation or Industry 4.0.
Sensor Classification
condenser microphone
A condenser microphone is also known as an electrostatic microphone; it consists of a film (the most common material is gold-plated polyester film; older products used to use very, very thin metal foil) near a solid metal plate that moves back and forth with respect to the solid backing plate when a sound wave strikes the film. In other words, the distance between the two capacitor pole plates changes. As a result, the capacitance changes with the rhythm of the sound wave, therefore converting sound into an electrical signal. Condenser microphones provide superior sound quality and typically offer higher sensitivity (i.e. output) and lower noise than moving coil microphones.

electret microphone
An electret is a permanently charged or polarized ferroelectric material and a type of condenser microphone. Electret microphones are suitable for inexpensive mass production, while expensive non-electret condenser microphones are of higher quality.
Unlike other condenser microphones, electret types do not require a polarization voltage, but they usually contain an integrated preamplifier. Due to their good performance and ease of manufacture, and therefore low cost, the vast majority of microphones manufactured today are electret microphones.

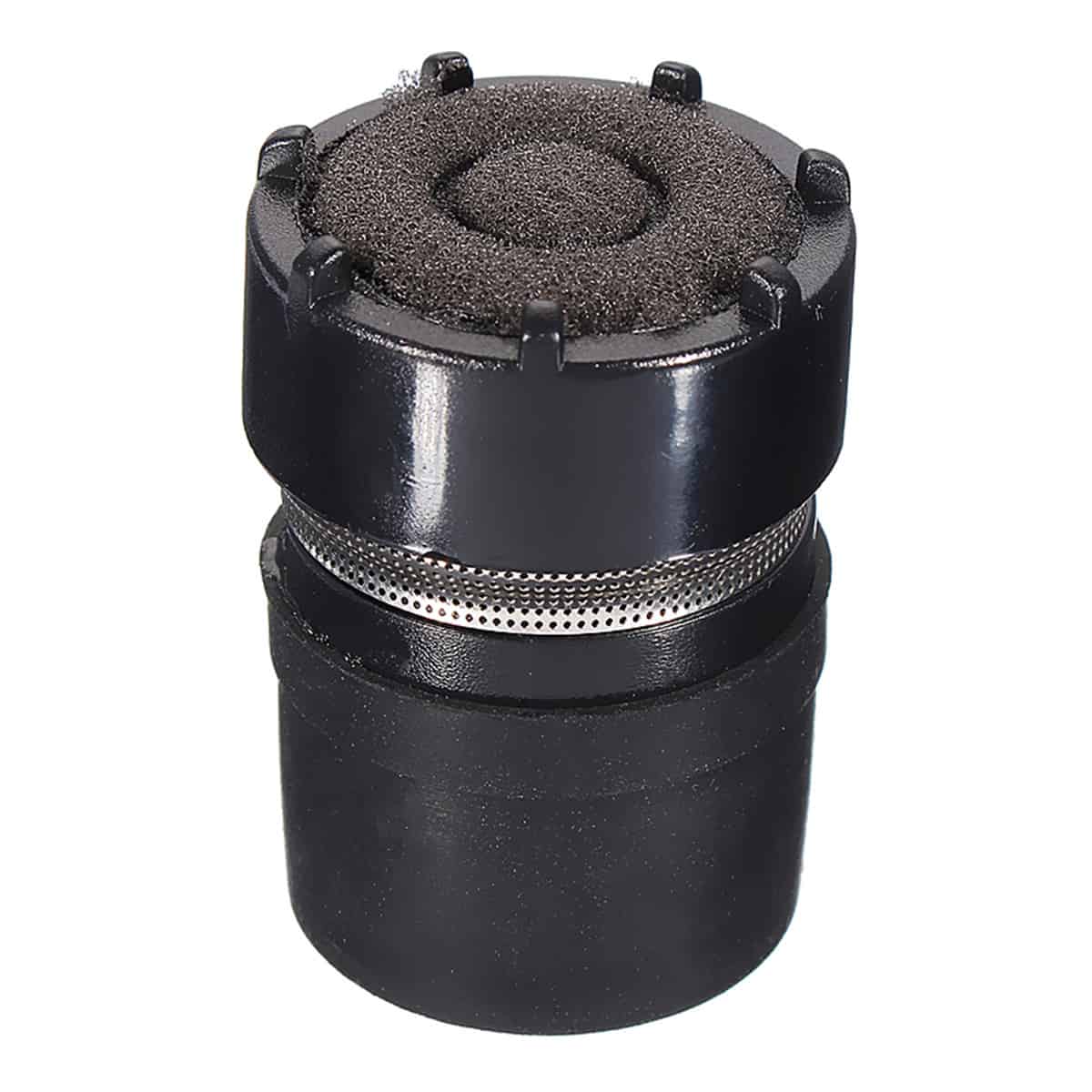
dynamic microphone
Dynamic microphones are microphones that convert sound into electrical signals through electromagnetism, and they're basically built like a loudspeaker: a coil is glued to the back of the film, and this coil is surrounded by a strong magnet. When a sound wave hits the microphone, the film moves in rhythm with the sound wave, and the coil on its back moves with it. The relative motion of the coil within its (fixed) magnetic gap induces a small signal voltage in that coil.
Dynamic microphones are usually better suited for use on stage because they are very rugged and do not require an external power supply.

ribbon microphone
Ribbon microphones use a thin, usually corrugated metal ribbon suspended in a magnetic field. The metal strip is electrically connected to the output of the microphone, and its vibration in the magnetic field produces an electrical signal. Ribbon microphones are similar to dynamic microphones in the sense that they both produce sound by magnetic induction. The sound output of a ribbon microphone is very honest and accurate.
Ribbon microphones are known for their delicacy and fragility, due in part to the extremely thin ribbon material suspended in the magnetic gap; a typical human hair is about 100 microns thick, but a ribbon microphone's ribbon material is only 0.6 microns thick.

carbon microphone
It consists of two metal plates separated by carbon particles. One plate is very thin and faces the speaker, acting as a diaphragm. Sound waves hitting the diaphragm cause it to vibrate, applying different pressures to the particles and thus changing the resistance between the plates. As the particles are pushed closer together, the higher pressure reduces the resistance. A steady DC current passes through the particles between the plates. The varying resistance leads to current modulation, producing a varying current that reproduces the changes in the sound waves.
Carbon microphones were the direct prototype of today's microphones and were vital to the development of the telephone, broadcasting and recording industries. Later, carbon particles were used between carbon buttons. Carbon microphones were widely used in telephones from 1890 through the 1980s.
laser microphone
Laser microphones are often portrayed in movies as spy gadgets because they can be used to pick up sound away from microphone equipment. The laser beam is aimed at a window or other flat surface that is affected by the sound. Vibrations in that surface change the angle at which the beam is reflected and the motion of the laser dot from the returning beam is detected and converted into an audio signal.
The possible operating range is up to 450 meters in open spaces and 200 meters in urban conditions. We can be bugged without even realizing it.
microelectromechanical systems

Microelectromechanical The MEMS (microelectromechanical systems), also known as silicon microphones, have a pressure-sensitive diaphragm etched directly onto a silicon wafer by MEMS processing technology, usually with an integrated preamplifier. Most MEMS microphones are variations of condenser microphone designs. Digital MEMS microphones have analog-to-digital converter (ADC) circuitry built into the same CMOS chip, making the chip a digital microphone and therefore easier to integrate with modern digital products.
Our company has been the agent of KNOWLES silicon microphone for more than 10 years, MEMS microphone is suitable for the mass production of end products, and the price has been getting cheaper and cheaper.
Sensor Manufacturers
There are many manufacturers of microphones, here are only some of the silicon microphone companies to do some listings
- Lou's (Knowles Electronics), USA
- China GOERTEK Acoustics (GOERTEK)
- China Ruixing Technology (AAC)
- Korea BSE
- Italy STMicroelectronics STMICRO
- Adeno Semiconductor (ADI)
- Hosiden (Japan)
- Cirrus Logic
- NeoMEMS (Wuxi)
- Bosch, Germany
Related resources
Content review.






