summarize
existIndustrial IoT SensorsThe team, we need to monitor the gas and liquid pollution, most of the use of chemical sensors, such as widely used in a variety of gases such as fire, smoke and other monitoring, as well as the monitoring of drunken driving, formaldehyde and carbon dioxide concentration in the air environment, the emission of pollution are all kinds of chemical sensors figure.
There are also many scenarios where chemical sensors are used in medicine, and some of the most portable biomolecular sensors you may know of are related to fertility measurements: pregnancy tests and ovulation tests. Both of these chemical sensors detect the presence of certain hormones in the urine. In the case of a pregnancy test, the sensor looks for the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the urine. Often these chemical sensors have a colorimetric component, so when the analyte (in this case hCG) binds, it triggers a color change in the sensor, making the reading of the results very simple.

A chemical sensor is a device that converts chemical information (composition, presence of specific elements or ions, concentration, chemical activity, partial pressure ......) into an analytically useful signal
A chemical sensor consists of a recognition section and a transducer section. The recognition section interacts with the target molecule or ion in the sample and the transducer converts the chemical interaction into a measurable signal.
About the partial pressure:
In a gas mixture, each component gas has a partial pressure, the nominal pressure of that component gas, as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of the thermodynamic activity of the gas molecules.
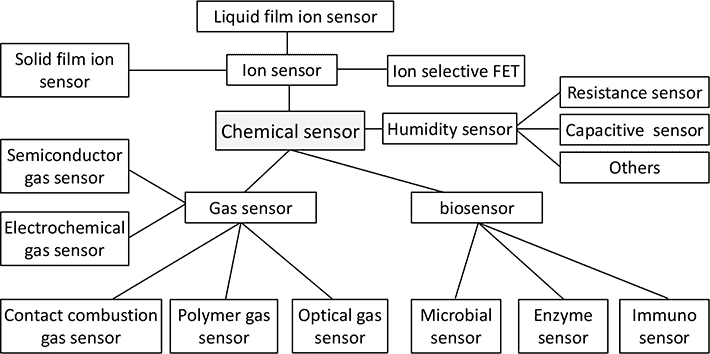
Sensor Classification
- Breathalyzer A breathalyzer or breathalyzer is a device used to estimate blood alcohol content (BAC) from a breath sample.
- Carbon Dioxide Sensors Carbon dioxide sensors or CO2 sensors are instruments used to measure carbon dioxide gas.The most common principles of CO2 sensors are infrared gas sensors (NDIR) and chemical gas sensors. Measuring carbon dioxide is important for monitoring indoor air quality, lung function in the form of CO2 mapping devices, and many industrial processes.
- Carbon Monoxide Detectors A carbon monoxide detector or carbon monoxide detector is a device that detects the presence of carbon monoxide (CO) gas to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. In the late 1990s, Underwriters Laboratories changed its definition of a single-station CO detector with an audible device to a carbon monoxide (CO) alarm. This applies to all UL 2034-compliant CO safety alarms [1]; however, for UL 2075-compliant passive indicators and system devices, UL refers to them as carbon monoxide detectors.
- Catalytic Bead Sensors Catalytic bead sensors are sensors for the detection of combustible gases and belong to the family of gas sensors called pellistors.
- ChemFET ChemFET is a chemically sensitive field effect transistor, which is a field effect transistor used as a sensor for measuring the chemical concentration in a solution. When the concentration of the target analyte changes, the current through the transistor changes accordingly. Chemoresistor A chemoresistor is a material that changes its resistance in response to changes in the nearby chemical environment.
- Chemoresistors are a class of chemical sensors that rely on a direct chemical interaction between the sensing material and the analyte. Several different materials have chemoresistive properties: metal oxide semiconductors, some conductive polymers and nanomaterials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. Typically, these materials are used as partially selective sensors in devices such as electronic tongues or electronic noses.
- Electrochemical Gas Sensors An electrochemical gas sensor is a gas detector that measures the concentration of a target gas by oxidizing or reducing it at an electrode and measuring the resulting current.
- An electronic nose is a device designed to detect odors or tastes. The term "electronic sensing" refers to the ability to reproduce human senses using sensor arrays and pattern recognition systems. The stages of the recognition process are analogous to the human sense of smell, and are used for identification, comparison, quantification and other applications, including data storage and retrieval. The stages of the recognition process are analogous to the human sense of smell and are used for identification, comparison, quantification and other applications, including data storage and retrieval.
- Electrolyte-Insulator-Semiconductor Sensors An electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor (EIS) sensor is a sensor that consists of three components: an electrolyte with the chemical substance that is to be measured, an insulator that allows for field-effect interactions with no leakage current between the other two components, and a semiconductor that records chemical changes.
- Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy It is an analytical technique used for elemental analysis or chemical characterization of samples. It relies on the interaction of certain X-ray excitation sources with the sample. Its characterization ability is due in large part to the underlying principle that each element has a unique atomic structure that permits a distinct set of peaks to appear on its electromagnetic emission spectrum. It is known by a number of acronyms, such as EDS, EDX, EDXS, or XEDS, and is sometimes referred to as energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDXA) or energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDXMA)
- Fluorescent Chloride Sensors Fluorescent Chloride Sensors are used for chemical analysis. The discovery that chloride (Cl-) is involved in physiological processes stimulated the development of intracellular Cl- measurement and fluorescence tools in living cells Holographic Sensors
- A holographic sensor is a device containing a hologram embedded in a smart material that detects certain molecules or metabolites. This detection is usually a chemical interaction that is converted into a change in a property of the holographic reflection (e.g., in a Bragg reflector), i.e., the refractive index or the spacing between holographic stripes. The specificity of the sensor can be controlled by adding molecules to the polymer membrane that selectively interact with the molecule of interest.
- Hydrocarbon Dewpoint Analyzer Dewpoint analyzers measure the moisture content of a gas to determine the theoretical temperature at which moisture condenses in the gas (saturation point)
- Hydrogen Sensors Hydrogen sensors are gas detectors that detect the presence of hydrogen. They contain miniature manufactured point-contact hydrogen sensors for locating hydrogen leaks. They are considered to be low cost, compact, durable and easy to maintain compared to conventional gas detection instruments Hydrogen Sulfide Sensors
- A hydrogen sulfide sensor or H2S sensor is a gas sensor used to measure hydrogen sulfide. It is used to detect hydrogen sulfide in fuel cell hydrogen feed streams to prevent catalyst poisoning and to measure the quality of the protective bed used to remove sulfur from hydrocarbon fuels. The hydrogen sulfide sensor is used in personal protective equipment to warn of the presence of hydrogen sulfide gas, for example in acid gas production sites.
- Infrared Point Sensors Infrared point sensors are point gas detectors based on non-dispersive infrared sensor technology. Toxic gases are measured in the low parts per million (ppm) range. Combustible gases are measured in the range 0 - 100% Lower Flammable Limit (LFL) or Lower Explosive Limit (LEL).
- Ion Selective Electrodes Ion Selective Electrodes (ISE), also known as Specific Ion Electrodes (SIE), are sensors that convert the activity of specific ions dissolved in solution into an electrical potential. According to the Nernst equation, the voltage theoretically depends on the logarithm of the ionic activity. Ion-selective electrodes are used in analytical chemistry and biochemical/biophysical studies where measurements of ion concentrations in aqueous solutions are required.
- Non-Dispersive Infrared Sensor A non-dispersive infrared sensor (or NDIR sensor) is a simple spectral sensor commonly used as a gas detector. It is non-dispersive in the sense of being optically dispersive, as the infrared energy is allowed to pass through the atmospheric sampling chamber without distortion.
- Microwave Chemical Sensors Microwave Chemical Sensors or Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) sensors consist of an input sensor, a chemisorbed polymer membrane, and an output sensor on a piezoelectric substrate, usually quartz.SAWS have been able to differentiate between organophosphates, chlorinated hydrocarbons, ketones, alcohols, aromatics, saturated hydrocarbons, and water.
- NOx Sensors A nitrogen oxide sensor or NOx sensor is typically a high temperature device used to detect nitrogen oxides in combustion environments such as car or truck exhausts or smokestacks.
- Olfactometer An olfactometer is an instrument used to detect and measure odor dilution. Olfactometers are used with human subjects in a laboratory setting and are most commonly used in market research to quantify and characterize the human sense of smell. Olfactometers are used to measure the odor detection threshold of a substance. To measure intensity, the olfactometer introduces an odorous gas as a baseline against which other odors are compared. An olfactometer is also a device used to produce aromas in a precise and controlled manner
- Optical Poles An optical pole or photopole is an optical sensor device, usually used to make optical measurements of specific substances with the help of a chemical sensor. Optical sensors are becoming increasingly popular due to their low cost, low power requirements and long-term stability. They offer a viable alternative to electrode-based sensors or more sophisticated analytical instruments, especially in the field of environmental monitoring
- Oxygen Sensors Oxygen sensors (or lambda sensors, where lambda is the air-fuel-equivalent ratio, usually denoted by λ) are electronic devices that measure the proportion of oxygen (O2) in an analyzed gas or liquid.
- Ozone Monitors Ozone monitors are electronic devices that monitor ozone concentrations in the air. The instrument can be used to monitor ozone values in industrial applications or to determine the amount of ambient ozone at ground level and to determine if these values violate the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS).
- A Pellistor pellistor is a solid-state device for detecting gases that are flammable or have a thermal conductivity significantly different from air. The word "pellistor" is a combination of particle and resistor.
- pH Glass Electrodes Glass electrodes are ion-selective electrodes made from doped glass films that are sensitive to specific ions. The most common application of ion-selective glass electrodes is the measurement of pH. pH electrodes are an example of glass electrodes that are sensitive to hydrogen ions. Glass electrodes play an important role in chemical analysis and physical chemistry research instruments. The voltage of a glass electrode is sensitive to changes in the activity of a certain ion relative to some reference value.
- Potentiometric Sensors Potentiometric sensors are chemical sensors that can be used to determine the analytical concentration of certain components in an analyte gas or solution. These sensors measure the potential of an electrode in the absence of voltage.
- Smoke Detectors A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, usually as a fire indicator. Commercial security devices signal to a fire alarm control panel as part of a fire alarm system, while home smoke detectors, also known as smoke alarms, usually emit a local audible or visual alarm from the detector itself.
- Zinc Oxide Nanorod Sensors A zinc oxide nanorod sensor or ZnO nanorod sensor is an electronic or optical device used to detect the presence of certain gas or liquid molecules in the ambient atmosphere. The sensor utilizes the enhanced surface area (and therefore surface activity) inherent in all nano-sized materials, including ZnO nanorods. The adsorption of molecules on the nanorods can be detected by changes in the nanorod properties, such as photoluminescence, conductivity, vibrational frequency, mass, and so on. The simplest and most popular method is to pass an electric current through the nanorods and observe the changes upon contact with a gas.


Sensor Manufacturers
- ALPHASENSE, UK
- BASELINE-MOCON, USA
- Austria AMS(APPLIED SENSOR)
- CAMBRIDGE CMOS SENSORS (UK): Acquired by AMS
- UK CITY TECHNOLOGY: Honeywell Subsidiary
- UK CLAIRAIR
- Korea ELT SENSOR
- Japan FIGARO (Figaro Giken)
- China Hanwei (Chinese company)
- China Huagong Technology
Related resources
Content review.





