-
×
 UWB Outdoor Wireless Base Station WE-RA220-O
1 × ¥3,449
UWB Outdoor Wireless Base Station WE-RA220-O
1 × ¥3,449
summarize
M-Bus (Meter-Bus) is a European standard (EN 13757-2physical and link layers.EN 13757-3Application Layer) for remote meter reading, gas meters, electricity meters or other types of consumption meters such as heating systems or water meters.The M-Bus interface is used to communicate over two lines and is therefore cost-effective.The radio variant of M-Bus Wireless M-Bus is also available in theEN 13757-4specified in
M-Bus belongs to the fieldbus family and consists of an information transmission system based on a common transmission medium to which devices capable of receiving and sending information are connected. The information is encoded in digital form and transmitted as data telegrams in serial mode. The transmission mode is asynchronous, half-duplex and is controlled by the master device. The transmission medium consists of a simple two-core cable to which all devices are connected in parallel.
M-Bus is an open system: the technical specifications and communication protocols are publicly available. Therefore, M-Bus devices from different manufacturers can be connected and exchanged on an M-Bus network.M-Bus is a master-slave system; communication is controlled by a single device (the master), which cyclically interrogates other devices (the slaves) to gather information. Slave devices cannot initiate communication, but must wait to be asked by the Master device. In addition to the data concentrator function, the Master usually provides other functions such as data storage (data logger) and remote control via a communications interface.
Development History
M-Bus by Paderborn University of Dr. Horst Ziegler and TI's Deutschland GmbH and TechemGmbH jointly proposed, M-Bus bus concept based on the ISO-OSI reference model, but M-Bus is not really a network. In the seven-layer network model of OSI, M-Bus only defines the functions of the physical layer, link layer, network layer and application layer. Since the ISO-OSI reference model does not allow the previous layer to change parameters such as baud rate, address, etc., M-Bus defines a management layer outside of the seven-layer model, which can be managed at any level without adhering to the OSI model. M-Bus meets the needs of utility instrumentation for networking and remote meter reading, and it also meets the special requirements of remote power supply or battery-powered systems. the bus topology of M-Bus serial communication is well suited for reliable, low-cost networking of utility instrumentation, and hundreds of slave devices can be connected over a distance of several kilometers.
Technical characteristics
- A bus cable connects all instruments to the central system, which is a very simple protocol.
- Select bus nodes are powered directly through the two-wire bus.
- All data can be read remotely and electronically.
- Minimal read errors, very fast reading speed, easy further processing
- Devices from different manufacturers can be connected to the bus system, which does not tie the user to the meter manufacturer
- All meters are individually addressable and in this way each energy meter can be controlled while using only one cable for connection.
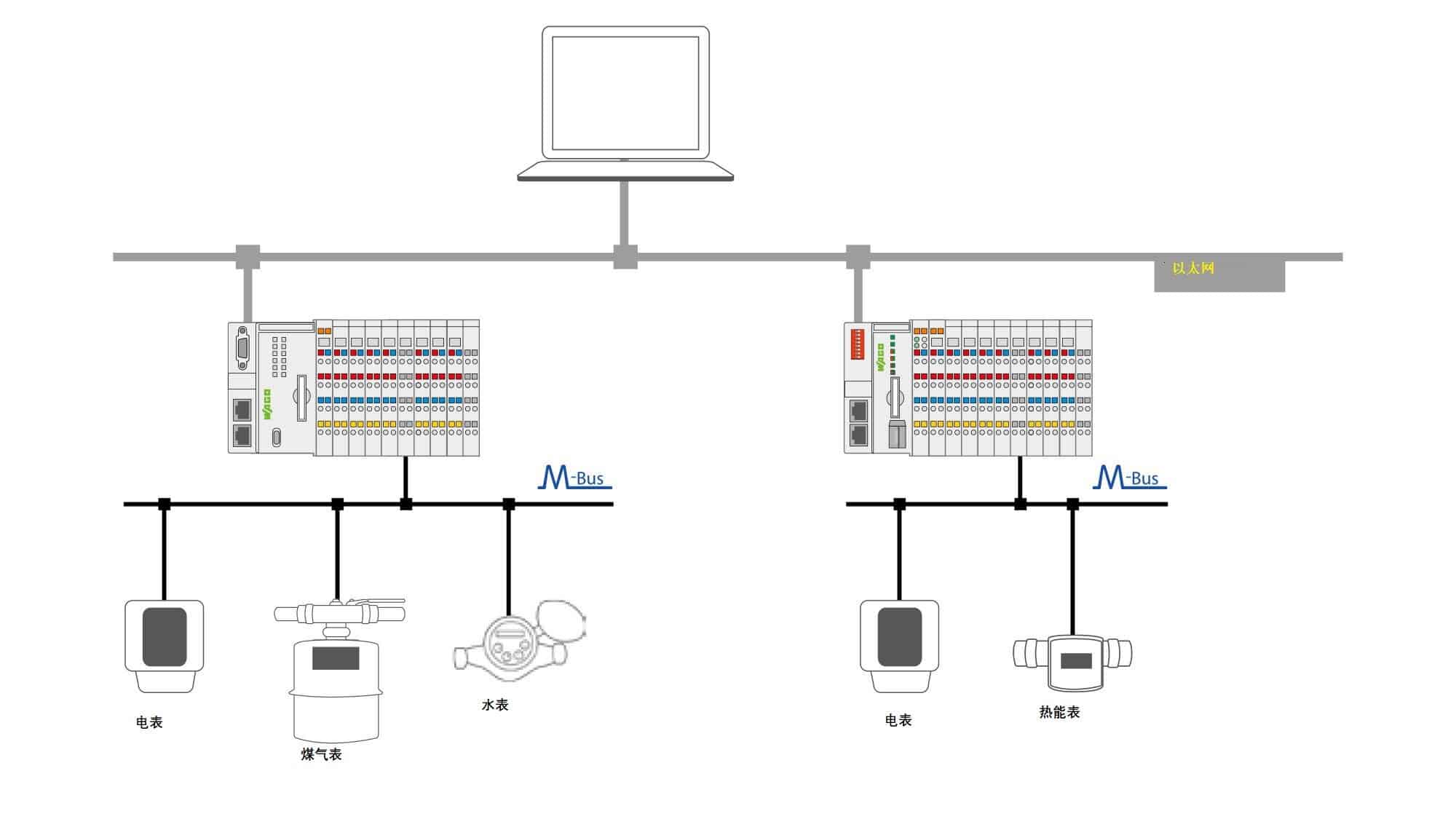
Application Areas
M-bus can be used in industry and, moreover, is easy to use in private households. According to the standard, the M-bus master can read up to 250 slave devices.
They can be heat, water, electricity or gas meters. You can also use M-bus in applications such as alarm systems, flexible lighting fixtures, heating controls, etc. It can monitor different consumption meters and can monitor any leaks!
Related links
Beijing Kehui Mingyuan Automatic Control Technology Co.: A range of M-Bus products that have been working on this technology for many years.
Modbus_Application_Protocol.pdf
Editor-in-chief of the website.
Content review.
Content review.





