summarize
Location-related information is one of the most fundamental elements of IoT applications and has a very wide range of application scenarios in indoor environments, such as personnel navigation in large buildings such as airports, tracking of special valuables, location-based services or advertisement push, security and intrusion detection and prevention. Among the manyIndoor positioning technologyBecause of the popularity of smartphones and tablet PCs, WiFi has a lot of natural advantages in indoor positioning scenarios. In general, WiFi hotspot, also known as AP (Access Point), or the location of the wireless router are fixed, hotspot only need to power, no matter how it encrypted, are bound to transmit signals to the surrounding area, as long as the device can be swept, do not need to connect to the WiFi, the location of the end of the hotspot can be detected to send the information to the server, the server based on the information, query, arithmetic, it will know the specific location of the client.

History of WiFi
During World War II, for military purposes scientists invented a military communications system that could withstand radio wave interference, which was called "Spread Spectrum Communications Technology", the predecessor of CDMA; Wi-Fi originated in Hawaii in 1971, where it uses a technology known as "Wi-Fi.ALOHAnetof a wireless UHF packet network to connect the islands, a protocol later developed by NCR and AT&T in 1991 called theWaveLANIn 1990, Sullivan, an Australian radio astronomer, researched that radio signals and wired network signals can be transmitted as fast and stably as possible, and since then WiFi has emerged as one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century. 1999, several visionary companies formed the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA); in October 2002, it was renamed the Wi-Fi Alliance (WECA); and in October 2002, it was renamed the Wi-Fi Alliance (WECA). Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (abbreviated as WECA); in October, 2002, it was renamed as Wi-Fi Alliance (abbreviated as Wi-Fi-Alliance).Wi-Fi Alliance), currently owns the Wi-Fi registered trademark. It clearly defines Wi-Fi as any "wireless local area network (WLAN) product based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 standard". Initially, Wi-Fi was used only as a replacement for the 2.4 GHz 802.11b standard, howeverWi-Fi AllianceThe generic use of the term Wi-Fi has been expanded to include any type of network or WLAN product based on any 802.11 standard, including 802.11b, 802.11a, etc.
Any products tested and approved by the Wi-Fi Alliance as "Wi-Fi Certified" (a registered trademark) are guaranteed to be interoperable with each other, even if they come from different brand manufacturers. This means that a user with a Wi-Fi Certified product can use any brand of router or modem with any other brand of client hardware that is also considered Wi-Fi Certified.
Certified products must have an identification stamp on the package that says "Wi-Fi Certified" and indicates the RF band used (2.5 GHz for 802.11b, 802.11g or 802.11n, 5 GHz for 802.11a), and the next generation of 802.11x standards is released every few years to improve performance and security. released every few years to provide improved performance and security.
groundWi-Fi AllianceThe global economic value of Wi-Fi is estimated at more than $3.3 trillion in a study commissioned. By 2025, that value is expected to grow to nearly $5 trillion.
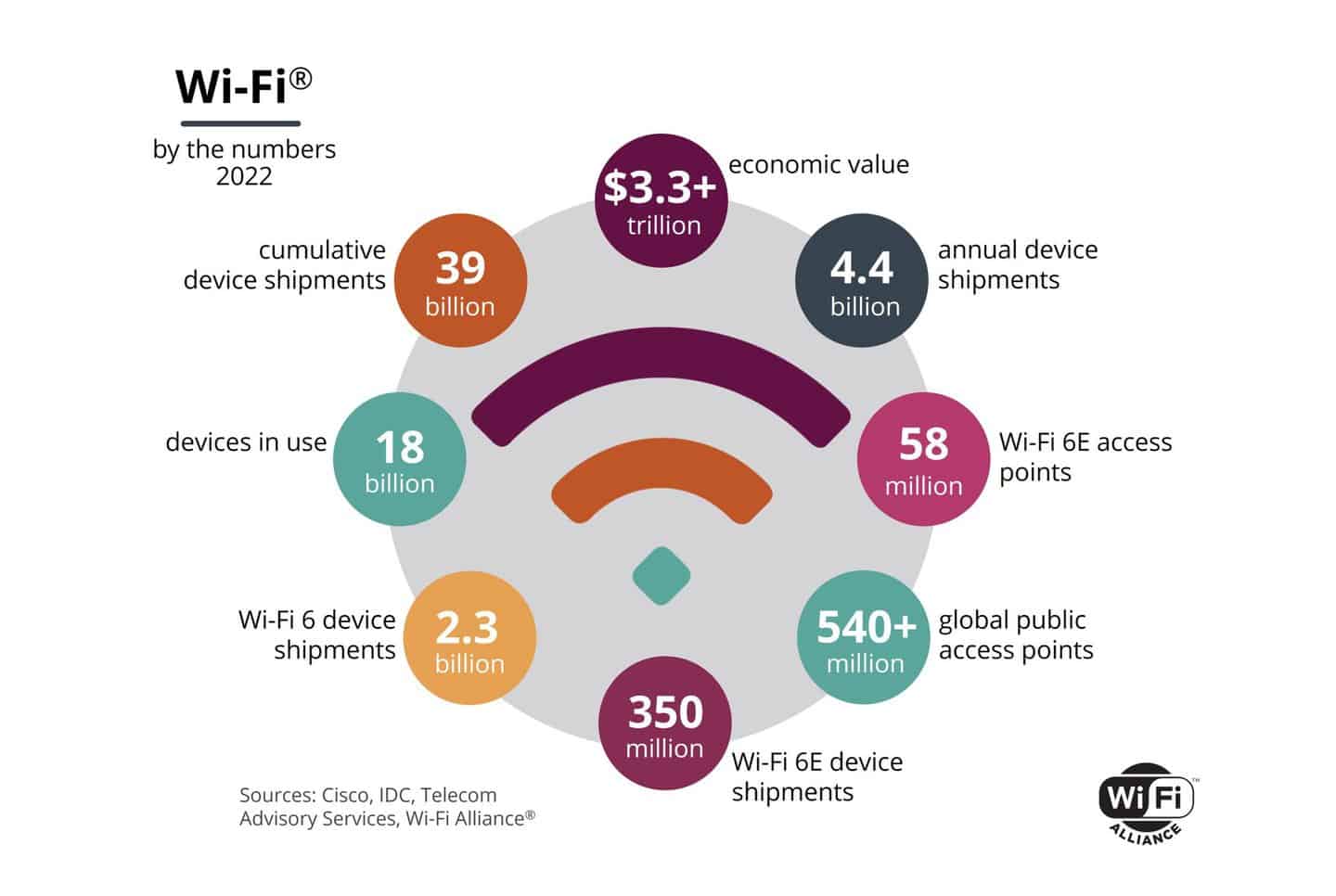
WiFi standard
To meet the demand for wireless access, theInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers IEEE(Institute of Electrical and ElectronicsEngineers,) from 2014 began to develop a new wireless access standard IEEE 802.11ax, in order to better popularize and promote, in October 2018, by the Wi-Fi Alliance on the different Wi-Fi standards developed a new naming, IEEE 802.11ax protocol standard is named Wi-Fi 6, and the previous 802.11n/ac is also renamed as Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5, which unifies the way Wi-Fi labeling is presented.Wi-Fi 6 is currently the latest version of the IEEE 802.11 WLAN standard and is upwardly compatible with the 802.11a/b/g/n/ac protocol standard. So to be precise WiFi is a brand, a trademark of the WiFi Alliance, but the standard has been renamed using a number in order to make it easier for Wi-Fi users and device vendors to understand and remember the Wi-Fi standard.
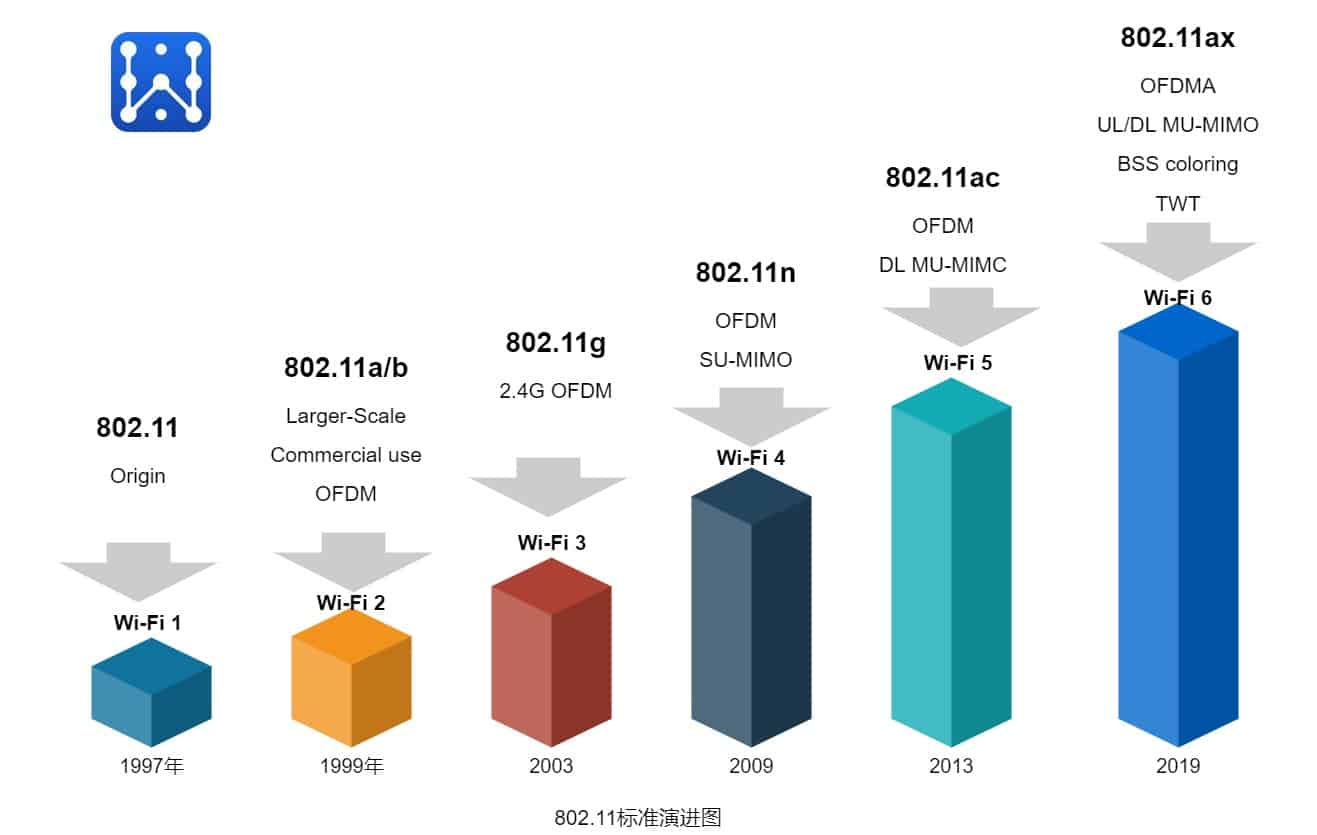
The latest Wi-Fi 6 standard is characterized by: first, high-speed transmission, the fastest single-stream rate of 1,201 Mbit/s under 160 MHz channel width, with a theoretical maximum data throughput of 9.6 Gbps; second, high energy efficiency, the router can unify the scheduling of the time of the wireless terminal hibernation and data transmission; and third, a wide range of coverage, supporting both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands at the same time. frequency bands, the 2.4 GHz band has a better signal than the 5 GHz band and better ability to penetrate walls.
Core technology of Wi-Fi 6
OFDMA
Wi-Fi 6 draws on the OFDMA technology (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) used in cellular networks, which allows data to be transmitted to multiple devices at once, allowing multiple carriers to transmit multiple packets at the same time in a single time period without the need for devices to queue up and compete with each other, thus Improve efficiency and reduce latency. Can be used in high-density environments with low throughput or small packet applications (e.g., IoT sensors)
MU-MIMO
MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), compared with Wi-Fi 5, which can only use SU-MIMO (Single-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) technology in the downlink, Wi-Fi 6 supports the full version of MU-MIMO technology, which supports both uplink and downlink, and can support 8 terminal devices to transmit data uplink and downlink at a time. Compared to Wi-Fi 5, which can only use SU-MIMO (Single-User Multiple-InputMultiple-Output) technology in the downlink, Wi-Fi 6 supports the full version of MU-MIMO technology, which supports uplink/downlink at the same time, and it can also support uplink/downlink data transmission of up to eight end devices at a time. Wi-Fi 6 allows the router to utilize multiple antennas to communicate with multiple end devices at the same time, making it "multi-purpose" and solving the problem of network congestion and slow network speed caused by multiple devices connecting at the same time.
1024-QAM modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a highly developed modulation scheme used in the communications industry where data is transmitted over radio frequencies. For wireless communications, QAM is a signal in which two carriers (two sinusoids) shifted 90 degrees out of phase (one-quarter phase) are modulated, producing an output consisting of amplitude and phase variations. These variations form the basis of the binary bits (the atoms of the digital world) that are transmitted.Wi-Fi 6's 1024-QAM allows data to be sent and received more closely together, allowing more information to be transmitted on the same signal, with a speed increase of up to 251 TP3T compared to Wi-Fi 5's 256-QAM.Wi-Fi 6 also utilizes both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, allowing multi-band transmissions. Wi-Fi 6 can also utilize both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, reducing network congestion with multi-band transmissions.
TWT
TWT (Target Wake Time) enables devices to determine when and how often to wake up to send or receive data. Essentially, this allows 802.11ax access points to effectively increase device sleep time and significantly extend battery life, a feature that is particularly important for the Internet of Things. In addition to saving power on the client device side, the target wake-up time allows wireless access points and devices to negotiate and define specific times for accessing the medium. This helps optimize spectrum efficiency by reducing contention and overlap between users.
BSS Coloring
Basic Service Set (BSS) Coloring marks shared frequencies to allow 802.11ax access points to determine whether simultaneous use of spectrum is allowed. Traditional high-density Wi-Fi deployments often assign multiple access points to the same transmission channel due to limited spectrum - an inefficient paradigm that leads to network congestion and slowdowns. Wi-Fi 6's BSS coloring technology reduces interference due to congestion and ensures consistent service for multiple connected devices in high-density environments. services for multiple connected devices in high-density environments.
WiFi positioning
The WiFi protocol was not originally designed for positioning, the single antenna, small bandwidth, and complex signal propagation environment indoors make traditional time-of-arrival/time-difference-of-arrival (TOA/TDOA) based ranging methods difficult to implement, Wi-Fi is one of the commonly used technological choices for calculating the location of real-time location system (RTLS) asset tags, and is not as popular as other positioning technologies such asbluetooth,Ultra Wide Band (UWB) or ultrasound) has advantages and limitations for the use of Wi-Fi indoor positioning systems. Some customers, particularly users of healthcare RTLS, have found that using existing Wi-Fi systems is problematic for achieving the accuracy goals required for their RTLS solutions.Wi-Fi is used for location determination in four different ways, each with its own set of advantages and challenges; in particular, WiFi positioning requires that the devices all require a module to act as a transceiver, which also results in a higher power consumption. Higher.
Wi-Fi fingerprint recognition
Empirical Fingerprinting assumes that, ideally, each geographic location in the target environment possesses a unique distinguishable radio signal signature that serves as the fingerprint information for that location; the degree of similarity of different fingerprints is strongly correlated with the physical distance between them.
The fingerprint-based localization process can be divided into two stages:
Offline training phase: Trainers hold mobile devices at multiple locations in the target environment to collect Wi-Fi signal strength information from different access points (APs).
Online positioning stageThe mobile device to be localized collects the Wi-Fi signal strength, forms a fingerprint vector at the location and uploads it to the server. The server side matches the reported fingerprint vector with each fingerprint record in the database through the fingerprint similarity matching algorithm, and finally determines the estimated location of the device to be located and sends it back to the mobile device.
The advantage of fingerprinting is that it is a cheap and simple method of obtaining location information from the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure; the main disadvantage is that changes in the environment, such as movement of furniture or equipment in the area, open/closed doors, or even people passing by may require recalculation of the predefined signal strength.
Fingerprint recognition + RSSI
An improvement on simple fingerprinting is the use of RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) based multilateralization, which uses the signal strength of all detectable Wi-Fi APs and their location knowledge to calculate the location.The RSSI (or Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the WiFi signal is inversely proportional to the distance, and combined with the trilateral measurements, RSSI can be used to approximate the location of an asset. In most cases, assuming sufficient APs, this can be accurate to around 4m or room level, however, due to obstacles and/or reflections, the measured RSSI of the signal may be reduced, resulting in inaccurate RSSI measurements and thus location determination
WiFi-TOF
Triangulation based on Time of Flight (ToF), i.e. when packets sent to the asset tag have multiple Wi-Fi AP timestamps. If the APs have tightly synchronized clocks, the time difference can be used to calculate the location. These systems require specialized Wi-Fi infrastructure that must be installed in a sufficiently dense layout to support RTLS. these systems are the most accurate but require expensive Wi-Fi systems. More APs need to be installed than are required for data-only use. Walls (especially in large buildings such as hospitals) may add multipath issues, which may reduce the accuracy of ToF-based RTLS
WiFi-AOA
Angle of Arrival (AoA) positioning, similar to ToF, where the angle at which a given Wi-Fi transmission is received is calculated using something called a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antenna, which clusters antennas together to increase range and throughput.MIMO antenna systems are common in some enterprise environments. Sometimes the system uses a combination of ToF and AoA, which can produce very accurate locations. there is an additional problem with AoA systems in that they need to be mounted in a certain direction in order to work properly. They have the same noise, sampling artifacts, and multipath channel effects as TOF, but the clock synchronization requirement is less of an issue
WiFi positioning manufacturers
Skyhooka company specializing in WIFI location algorithms, operates the world's largest independent location network, consisting of more than 4.5 billion geo-located Wi-Fi hotspots and more than 180 million geo-located cell IDs. Every day Skyhook processes tens of billions of location transactions, providing precise and accurate location data and intelligence to devices, apps, wearables, media, brands and advertising platforms, and has now been acquired by Qualcomm.
UFIThe core technology is ultra-low power Wi-Fi technology and high-precision real-time positioning and behavior analysis algorithms as well as related IoT products. UFI Wi-Fi IoT platform can realize location-based real-time status monitoring and refined management functions, integrating automatic identification (RFID), real-time localization (RTLS), wireless sensing (WSN), map navigation, data collection, voice and video transmission and other functions into one set of network and one platform. The company's products have been widely used in business, pension, industry, coal mine, medical, community, exhibition hall, security, supervision and other industries.
sensewhere's indoor positioning technology is based on an extensive patent portfolio. The software enables indoor positioning in areas with weak or blocked GPS satellite signals, such as indoors or in dense urban areas, without the need for additional infrastructure; Tencent Maps has selected sensewhere's indoor positioning software as part of its location SDK, which is available to a wide range of users of Tencent's mobile platforms and Tencent-affiliated companies' mobile services. sensewhere's unique, highly scalable approach greatly enhances Tencent Maps' indoor positioning and location advertising capabilities, enabling users to navigate indoors in a more accurate and convenient manner
Inpixon IoT sensors have been developed to collect indoor data that detect and locate wireless devices to support location-based solutions. Versatile sensor series and modular sensors from wireless device detection and localization to visitor analysis, asset tracking and more.
Link LabsFounded by a group of engineers at Johns Hopkins University, it provides the industry's most complete end-to-end enterprise IoT platform for tagging, locating, and monitoring devices, supplies, and assets in the marketplace, and holds more than 25 patents for innovative solutions. Deploys hundreds of thousands of IoT devices and manages billions of IoT events every month.
WiFiSlam's main business is to enable smartphones to locate themselves indoors, and they have launched an application that allows smartphones to utilize existing WiFi hotspots in buildings to locate themselves. Acquired by Apple in 2013, Apple's acquisition of WifiSLAM should be mainly interested in the positioning algorithms behind it, which can be seen in the indoor positioning of its long-term layout.
Shanghai Tuju IntelligenceFounded in 2012, high-precision indoor map and indoor positioning technology services, is a provider of indoor map services and indoor positioning solutions. Listed on the New Third Board (stock code 837764) in 2016, becoming the first listed company in the indoor GIS industry.
Content review.





