summarize
interior positioningThere are many technical solutions:Ultrasonic signals,ultra-wideband technology,Bluetooth Low Power Technology,Wireless RFID networksof fingerprint identification methods, on-board sensors (monocular camera, stereo imaging and light detection and ranging). We can often see practical scenarios such as in: applications in warehouses, where automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are localized by triangulation based on reflector feature points detected by a laser scanner. or the attitude of a vehicle is estimated by examining the changes caused by the motion on the image acquired by the on-board camera; there is also the combination of signals generated by inertial sensors and wheel encoders using magnetic field maps to accurately position indoor robots without the need for any additional infrastructure; inertial sensors (accelerometers, rate gyroscopes combined with magnetometers), etc., can be used to estimate the angular position of the mobile robot, the speed or acceleration.
A linear positioning system based on infrared (IR) beacons is designed to locate indoor pedestrians using triangulation.The IR beacons are attached to a shopping bag and the receiver mounted at a height of 2.3 meters above the ceiling is a PD array which is used to measure the angle of incidence of the beacons rays.The IR beacons indoor position is then computed and the identifier signals are sent to a computer to be processed via wireless communication.
Definition of infrared
Rather than detecting infrared radiation, wireless infrared technology uses infrared radiation to transmit and receive data and commands. Probably one of the most common examples of wireless infrared technology is the television remote control. Sensors in the remote control transmit infrared lasers to sensors in the TV, which receive the relevant commands to operate the TV, turn it on, change the radio station, and so on.
There are typically two types of wireless infrared technology: directional and diffuse. Directional technology uses infrared lasers to transmit information, but there must be an unobstructed line of sight between the infrared light source and the receiver, with no obstructions. We often see scenes in blockbuster TV movies where the theft of a secret or a treasure requires a high degree of skill to avoid infrared beams, because these beams trigger a warning once they are blocked. Diffuse infrared technology scatters the beams, making them harder to block. The TV remote control is an example of diffuse infrared wireless technology, which should effectively control the TV as long as you are in the same room.
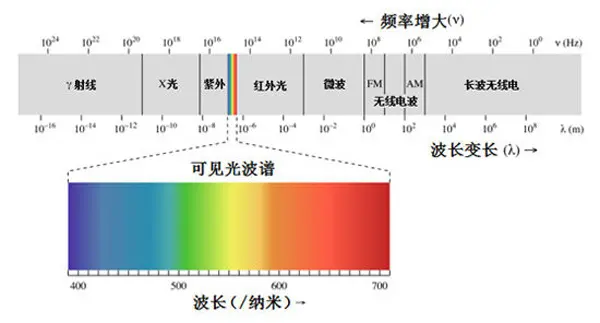
The visible light we see every day is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum includes all types of radiation, from X-rays used in hospitals to radio waves used for communication. Radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum is categorized by wavelength. Short-wavelength radiation, such as gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet light are high-energy and can be very dangerous; longer-wavelength radiation, such as radio, microwave, and infrared, is less harmful.
How infrared was discovered
In 1681, the pioneering experimentalistEdme Mariotteshowed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, blocks radiant heat; T he made outstanding contributions to optics, made a thorough study of light phenomena, wrote the paper "On the Nature of Colors," and introduced the 23° halo of angular radius and the concept of the blind spot
groundUS National Aeronautics and Space AdministrationThe claim that infrared light was discovered by British astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel in 1800. In an experiment to measure the temperature difference between colors in the visible spectrum, he used a prism to split sunlight into different spectra and placed a thermometer in the light path of each color in the visible spectrum; he noted an increase in temperature from blue to red and found that the temperature measurements were warmer beyond the red end of the visible spectrum. In the electromagnetic spectrum, infrared waves occur at frequencies higher than those of microwaves and just below those of red visible light, hence the name "infrared".
Infrared applications
Infrared radiation is used in industrial, scientific, military, commercial and medical applications. Night-vision equipment using active near-infrared illumination can observe people or animals without detecting the observer. Infrared astronomy uses telescopes equipped with sensors to penetrate dusty regions of space, such as molecular clouds, to detect objects such as planets, and to observe highly redshifted objects in the early universe. Infrared thermography is used to detect heat loss in insulation systems, to observe changes in blood flow in the skin, and to detect overheating of electrical components.
Military and civilian applications include target acquisition, surveillance, night vision, homing and tracking. Humans at normal body temperature radiate primarily at wavelengths around 10 μm (micrometers). Non-military uses include thermal efficiency analysis, environmental monitoring, industrial facility inspection, growth operation detection, remote temperature sensing, short-range wireless communications, spectroscopy and weather forecasting
See the chart below. The smaller the wavelength, the greater the capability and the greater the danger.

Short-wavelength infrared
Wavelength range of 1.4 to 3 microns. Mainly used for telecommunication and military purposes
Medium wavelength infrared
Wavelengths in the range of 3 to 8 microns, which are used in the chemical industry and astronomy
Long-wavelength infrared
With wavelengths ranging from 8 to 15 microns, astronomical telescopes and fiber-optic communications are possible with the help of long-wavelength infrared
far infrared ray
The wavelength range is 15 to 1000 microns. It is mainly used for cancer and tumor treatment.
Application of infrared technology for indoor positioning
In most cases, infrared light is invisible to the human eye, making the technique less invasive than visible light-based indoor localization. System architectures for positioning based on infrared signals vary widely, and the three general approaches to utilizing infrared signals are 1) the use of active beacons, 2) infrared imaging using natural (i.e., thermal) radiation, or 3) artificial light sources.
active beacon
The active beacon approach is based on stationary infrared receivers placed at known locations in the room space and mobile beacons with unknown locations. The system architecture can include only one receiver per room for simple room pinpointing, or one receiver with additional AoA capability for sub-room pinpointing. In order to achieve meter-level accuracy or better, the configuration of an active beacon-based IR tracking system must include several receivers deployed in each room to differentiate between areas of the room. Note that infrared signals cannot penetrate opaque materials such as walls and ceilings.
thermal radiation
Localization systems that use natural infrared radiation are known as passive infrared localization systems. Sensors operating in the long-wavelength infrared spectrum (8 micrometers to 15 micrometers, also known as the temperature recording region) are able to obtain a completely passive image of the surrounding world from natural thermal radiation. Therefore, there is no need for an active infrared illuminator or any other specialized heat source. Thermal infrared radiation can be used to remotely determine the temperature of a person or object without the need for a tag or transmitter. Existing thermal detectors are thermal cameras, broadband detectors, thermoelectric infrared sensors for motion detection or thermocouples for converting thermal gradients into electrical energy or for contactless temperature measurement. But there is one obvious disadvantage: passive infrared methods are compromised by strong radiation from the sun.
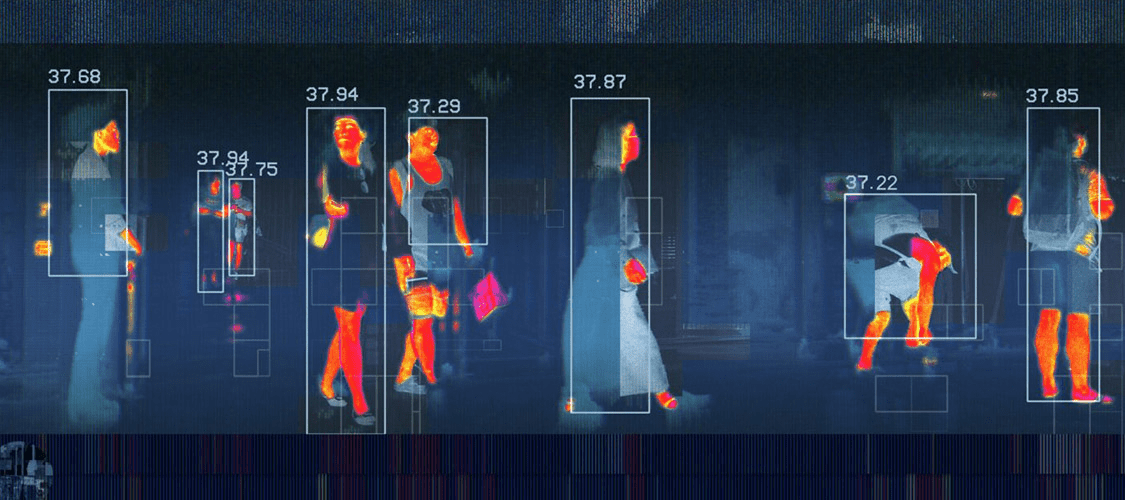
artificial light source
Optical infrared indoor positioning systems based on active infrared light sources and infrared sensitive CCD cameras are a common alternative to optical systems operating in the visible spectrum. Implementations using infrared cameras are either based on active infrared led
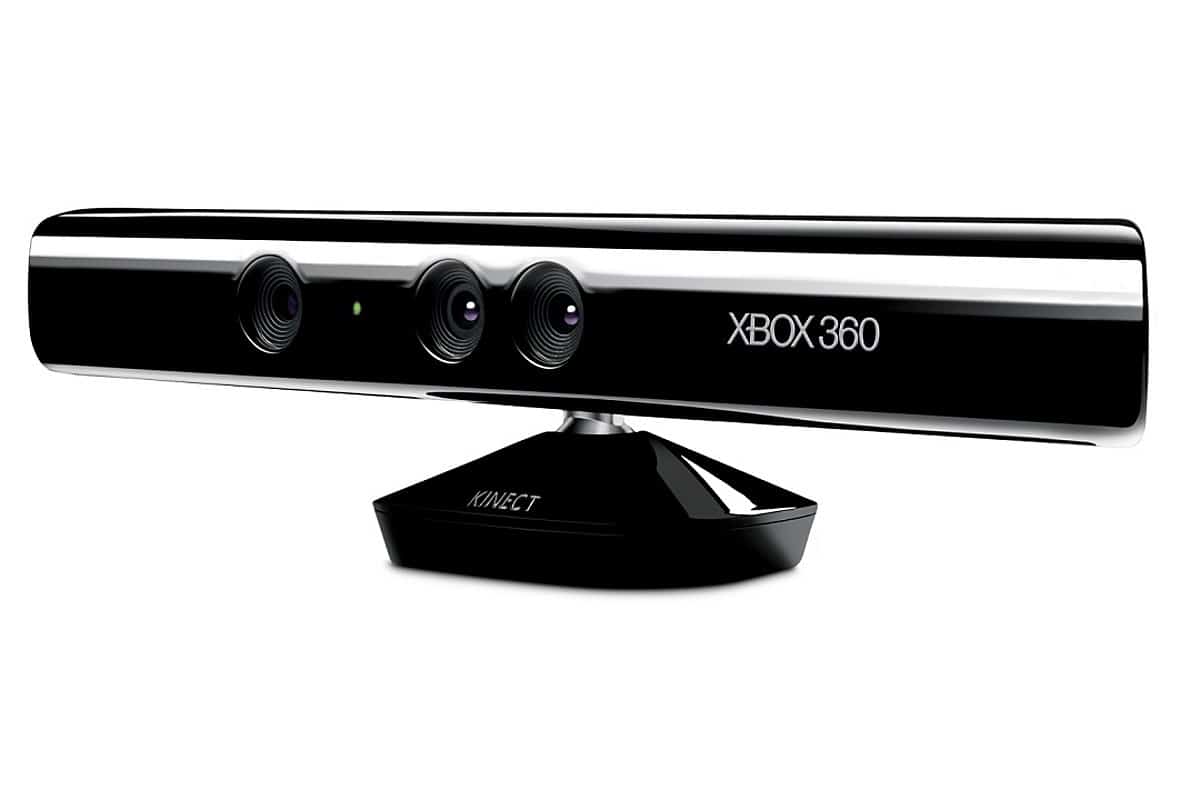
Video Game ConsolesXbox(Microsoft Kinect 2011) The motion sensing device Kinect uses continuously projected infrared structured light to capture 3D scene information via an infrared camera.The 3D structure can be calculated based on the distortion of a pseudo-random pattern of structured IR dots, and at a frame rate of 30 hertz can simultaneously track a person at a distance of 3.5 meters. Accuracy is reported to be 1 cm at a distance of 2 m. The release of the Kinect software development kit has inspired a number of third-party developments for automated tracking, robotic navigation and gesture control, and even surgical navigation. Developed byEvolution Robotics The Polaris system developed in (2010) is also based on the projection of infrared laser points, Polaris uses only two projection points to determine the position and orientation of the vacuum cleaner


Content review.





