Overview - the need for agreements
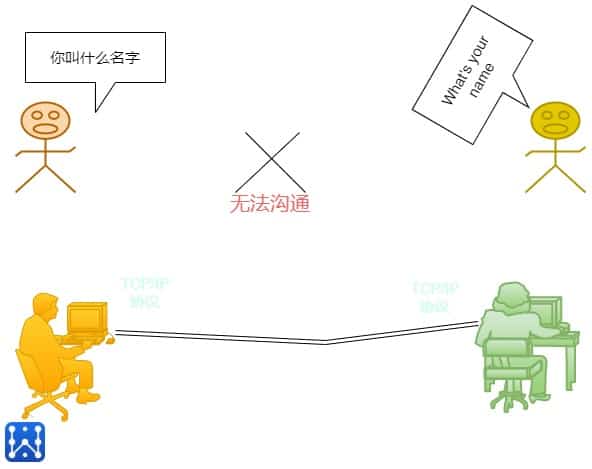
In the field of IoT and computer networking and information communication, we often refer to "communication protocolThe concept of "agreement". Simply put, it is a kind of "agreement" reached between the terminal and the terminal to realize communication through the network. This "agreement" makes it possible for computers of different manufacturers, different devices, and different operating systems to communicate with each other as long as they follow the same protocol. Conversely, if different protocols are used, communication is not possible.
Let's take an example, for example, if two people use different languages to communicate on the phone, they will not be able to communicate effectively even if they hear each other's voices.
Standardization and organization of agreements
In the initial stage of computer communications, systematic and standardized work has not been paid enough attention to, we do not have too much attention to the protocol, resulting in the development of the process of a lot of problems, resulting in each manufacturer to produce their own network products to achieve communication, from which it can be understood that the products of different vendors can not be communicated with, the user suffering, users use a certain manufacturer's products must be always used its Users using a vendor's products must always use its network products, otherwise it will not be able to use; if a vendor bankruptcy or product discontinued, the entire network equipment must be replaced. This leads to a waste of resources, and the speed of industrial development is greatly slowed down.
In 1974, IBM released SNA (IBM Systems Network Architecture) to publicize this systematic network architecture. Subsequently, various manufacturers released their own network systems, but due to the incompatibility of each manufacturer's architecture and protocols, it was still impossible to communicate effectively, and the network could not operate even if it was connected at the physical level.
In fact, in our lives, standardization is ubiquitous in our daily lives, power sockets, toilet paper, paper books, pencils and ballpoint pens, etc. There is no standard figure anywhere, imagine if there is no such standard, we buy toilet paper if there are various different sizes, how much trouble it will bring to our lives. With the network and computer world booming, we gradually realize the importance of compatibility, and for this reason ISO (International Organization for Standardization) has developed an international standard OSI (Open Communication System Interconnection Reference Model) to standardize the communication system.
There are three main types of standardization organizations: international standardization organizations (e.g.ISO,ITU-T), national standardization organizations (U.S.ANSI"China'sStandardization Administration of PRC (SAC)JapaneseJIS), civil standardization organizations (IETF(math.) genusIEEE). Many of the best companies in the real world do not make their development specifications public, thus preventing their technologies from becoming widely available, so standardization is a long-term and important task that will have a significant impact on the future of the world as a whole.
Protocol Layers and the OSI Reference Model
ISO in the development of standardized OSI, the network architecture related factors for a long time and fully numerous discussions, and finally put forward as a communication protocol design index of the OSI reference model, this model will be the necessary functions of the communication protocol for the layering, through which the whole complex network protocol more simple and clear.
In this reference model, each layer receives information and services from the next layer and is responsible for providing information and services to the next layer. The conventions for interaction between the upper and lower layers are called "interfaces". The conventions for interacting with information from one layer to another are called "protocols". Protocol layering isolates each layer for independent use, which allows for the construction of a scalable and flexible system.World PowerWe are committed to building a "Lego" model for IoT-based hardware, and we are using this thinking to expand our product line.
| storey | Layered name | Key Features | Main introduction of the function |
| 7 | application layer (computing) | Application-specific protocols | Application-specific protocols, such as SMTP for e-mail, SSH for remote login, FTP for file transfers |
| 6 | presentation layer | Conversion of device-intrinsic and network-standard data formats | Receive information in different formats, such as text, images, sound, etc. JPEG,MPEG |
| 5 | session layer | Communications management: establishing and disconnecting communications connections and managing sublayers below the transport layer | When to establish a connection. When to disconnect and how long to stay connected, e.g. RPC, SQL, NetBIOS |
| 4 | transport layer | Manage reliable data transfer between two terminals or nodes | Reliable transmission ensures that data is transmitted reliably to the receiving address. Examples include TCP, UDP, etc. |
| 3 | network layer | Address management and routing | Transmission of data to a destination address via routing and addressing, e.g. protocols such as IP, IPX, etc. |
| 2 | data link layer | Transmission and recognition of data frames between interconnected devices | Divide the sequence of 0s and 1s into meaningful data frames for transmission to the other party (Switch, Bridge), e.g. PPP, SLIP, Switch |
| 1 | physical layer | Define connector and network cable specifications | Responsible for the interchange of 0 and 1 bit streams with the voltage level and the brightness of the light (Hub, Repeater). |
Content review.





