Overview of Interface Types
Communication interface technology is a very important technology in the Internet of Things system, whether it is the interconnection of various types of communication networks, or a variety of terminal equipment into the network, as well as a variety of communication protocols, software adaptation and so on can not be separated from the technical specifications of the communication interface. For the definition of "interface", "Communication ScienceTechnical nameInterfaces can be described at the physical level, at the software level, or as purely logical operations. Physical interfaces are hardware interfaces between different devices and components. The interface is divided into wired and wireless, and wireless is mostly used in the form ofa radio frequencymethod of transmission.
IoT communication because it involves a variety of practical scenarios, we summarize the IoT communication interface types according to customer needs are probably several types, the first and second types are long-distance wireless communication, mainly based on thecellular communications technologyThe 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G andNB-IOTand non-cellular long-range wireless communications such asLora ,Sigfoxcommunication methods; the third category is short-range wireless communication, which mainly includesbluetooth,UWB,NFC,RFID,WIFI, andzigbeetechnology; the fourth category is wired communications, which are mainlyUSB,RS485,RS232,RS422various kindsserial port communication,Ethernetrespond in singingMBusMode of communication; WEC website screening method is basically carried out according to this, the following for these types of briefly do some introduction:
Category I: Cellular telecommunication
Cell phone communication technology
1G It was the first generation of mobile communication technology, a product of the analog-digital era, and could only be used for voice calls, but it brought about a sea change in the field of cell phones, and telephones began to transition from the corded to the cordless stage.1G is the analog telecommunication standard that was introduced in the 1980s and continued until replaced by 2G digital telecommunication.. -wikipedia A short sentence summarizes the product of this era.
2GSecond-generation cellular communications technology, centered on digital voice transmission technology. The user experience rate is 10 kbps, with a peak rate of 100 kbps.Generally defined as a cell phone communication technology specification that does not allow for the direct transmission of information such as email, software, etc.; only has the ability to make calls and some transmission such as time and date. Wikipedia explains:2G is short for second generation cell phone technology. It was the first version to become a digital standard and it replaced the analog 1G standard. It was replaced by 3G. Some countries have shut down their 2G networksThe
3G"Third-generation cellular communications technology specifications refer to a new-generation mobile communications system that combines wireless communications with multimedia communications, such as the international Internet. It is capable of handling various forms of media, such as images, music and video streaming, and providing a wide range of information services, including web browsing, teleconferencing and e-commerce. In order to provide such services, the wireless network must be able to support different data transmission speeds, that is, at least 2 Mbps (megabits per second), 384 kbps (kilobits per second), and 144 kbps (kilobits per second), respectively, in indoor, outdoor, and driving environments. Wikipedia notes:3G stands for Third Generation and is the third generation of wireless mobile communication technology. It was replaced by 4G.3G was introduced on March 3, 2003 and replaced in 2009The
4GThe fourth generation of mobile information systems is a better improvement on the 3G technology, and one of its major advantages over the 3G communication technology is that it combines WLAN technology and 3G communication technology, which makes the transmission of images faster, and the quality of the transmitted images and the images look clearer. A faster version called LTE (Long Term Evolution) became commonplace in the late 2010s. 2020 saw the introduction of a new standard called 5G. The use of 4G technology in smart communications devices allows users to access the internet more quickly, at speeds of up to 100Mbps.
5G The fifth generation of mobile communication technology, is a new generation of broadband mobile communication technology with high speed rate, low latency and large connection characteristics, 5G communication facilities is to realize the human-machine-thing interconnection of network infrastructure; the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defines three major categories of 5G application scenarios, namely, enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-high reliability and low-latency communication (uRLLC), and massive machine class communication (mMTC). . Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) is mainly oriented to the explosive growth of mobile Internet traffic, providing mobile Internet users with a more extreme application experience; ultra-high reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) is mainly oriented to the needs of industrial control, remote medical care, automatic driving and other vertical industry applications with extremely high requirements for delay and reliability; massive machine class communication (mMTC) is mainly oriented to the smart city, Smart home, environmental monitoring and other applications targeting sensing and data acquisition.
Low-frequency 5G is a type of 5G that uses low frequencies, just like 4G. Low-band 5G has a longer range (meaning you can be far away from a tower or inside a building and still get a signal) but is slower than other types of 5G. Low-band 5G is only a little faster than the LTE version of 4G. Low-frequency 5G usually has speeds of about 100 Mbit/s.
IF 5G is a type of 5G that is slightly higher in frequency than LF 5G. it has a shorter coverage area than LF 5G, but you can still usually get service indoors using IF 5G. IF 5G is much faster than LTE. Medium-frequency 5G typically has speeds of 600 Mbit / s to 1 Gbit / s. It can be used in a number of different ways.
Millimeter-wave 5G is a type of 5G that has a much higher frequency than low and intermediate frequencies. It has a very short range. With millimeter wave, you cannot get service inside buildings. Most solid objects can block millimeter waves. Millimeter waves are much faster than any other type of 5G and can currently reach speeds of up to 2 Gbit/s. Millimeter waves are considered the least practical version of 5G because the range is so short that basically anything can block it

NB-IoT
NB-IoTNarrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) has emerged as an important branch of the Internet of Everything.NB-IoT has a special focus on indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life, and high connectivity density.NB-IoT uses a subset of the LTE standard, but limits the bandwidth to a single narrow band at 200kHz. It uses OFDM modulation for downlink communications and SC-FDMA for uplink communications.NB-IoT is built on cellular networks, consumes only about 180kHz of bandwidth, and can be deployed directly on GSM networks, UMTS networks, or LTE networks; NB-IoT focuses on the low-power, wide-range (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market, and is an emerging technology that can be deployed worldwide. NB-IoT focuses on the low-power wide coverage (LPWA) IoT market and is an emerging technology that can be widely used worldwide. It is characterized by wide coverage, multiple connections, fast rate, low cost, low power consumption, and excellent architecture. Due to these features, applications are in the areas of parking, meter reading, firefighting, water hydrology, street lighting, bike sharing, and home appliances
Category II: Non-cellular wireless telecommunication
LoRa and LoRaWAN
LoRarespond in singingLoRaWANTogether, they define a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWA) network protocol designed to wirelessly connect battery-powered "things" to the Internet in regional, national, or global networks, and to address key Internet of Things (IoT) requirements such as two-way communication, end-to-end security, mobility, and localized services. Low power consumption, low bit rates, and the use of IoT distinguish this type of network from wireless WANs, which are designed to connect users or enterprises and transmit more data using more power.LoRaWAN data rates range from 0.3 kbit/s to 50 kbit/s per channel.

LoRa (long range Radio) it is a company in Grenoble, France Cycleo (patent 9647718-B2) development, later acquired by Semtech, its purpose is to solve the power consumption and transmission of difficult to cover the distance of the contradiction between the problem, it is the most important feature is in the same power consumption conditions than other wireless ways to propagate the distance is farther to achieve the unity of low power consumption and long distance, it is under the same power consumption than traditional wireless radio communication distance expanded by 3-5 times. The unification of low power consumption and long distance, it is under the same power consumption than the traditional wireless radio frequency communication distance expansion of 3-5 times.
LoRaWAN defines software communication protocols and system architectures.The continued development of the LoRaWAN protocol is supported by the open, non-profitLoRa Alliance ManagementSome of the members of the alliance are IBM, Everynet, Actility, MicroChip, Orange, Cisco, KPN, Swisscom, Semtech, A2A Smart City SPA, Bouygues Telecom, Singtel, Proximus, The Things Industries and Cavagna Group.
Its function is the same as that ofNB-IoTSimilarly, it just requires an autonomous network; it has been widely and successfully applied in many fields such as smart buildings, smart industrial parks, asset tracking, power and energy management, metering, fire fighting, smart agriculture and livestock management, epidemic prevention and control and medical healthcare, satellite applications, walkie-talkie applications, etc.
SigFox
Sigfox is a long-distance communication standard developed by the French company Sigfox in 2009, Sigfox uses ultra-narrow band modulation technology to transmit signals in the 192kHz spectral bandwidth of the public frequency band under the transmission of each message width of 100Hz, the power density per unit of the frequency band is high, and the anti-jamming capability is strong
Terminal devices send packets with Sigfox protocol, SIgfox base station receives the data and then passes it to SIgfox cloud, which then distributes the data to client servers to parse the application information. Its product features: very low battery power consumption, up to 10 years of life; easy to use, very easy and fast configuration between base stations and devices; low cost, SIgfox optimizes each link to reduce costs; user data is very small, up to 12B; customers can easily use it together with other communication solutions, strong collaboration.

It owns all the core technologies related to network construction, adopts the way of cooperation with telecom operators or self-built networks to deploy networks, and profits by controlling the network and the Cloud, from core technologies, to network construction, and then operation are a handful of, this way can not be recognized by the market, resulting in the declaration of bankruptcy in early 2022, and in May 2022 by the Singapore Internet of Things Operator.UnaBizThe end of the acquisition.
Category III: Short-range wireless communications
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi AllianceWi-Fi is any "wireless local area network" (WLAN) that follows the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 specification," the company said. Wi-Fi devices can work with any Wi-Fi network anywhere in the world.
Most wireless networks use one of two radio frequency bands. These are not the only two bands, but the most commonly used. One of the bands has a frequency of about 2.4 GHz, and the other has a frequency of 5 GHz.There are advantages and disadvantages to both: the 2.4 GHz band is widely used, and equipment is usually cheaper. Microwave ovens, DECT phones, and other wireless devices also use the 2.4 GHz band, which sometimes causes interference that slows down transmissions.The 5 GHz band has more frequencies and usually less interference, but there are more rules for using it. In some locations, the 5 GHz band may not be available for outdoor use. Because fewer devices use the 5 GHz band, devices that use the 5 GHz band are usually more expensive.

WIFI communication protocol plays a decisive role in the home, as devices can directly access the Internet through the WIFI protocol, resulting in the popularity of this application in the home; the direction of development of Wi-Fi / WiMAX includes: network technology, coverage of a greater range, from hot spots to hot zones to the entire city; Wi-Fi handheld terminals and VoWLAN services will inevitably become a potential application mode. Therefore, the coverage of commercial WiFi in urban public transportation, shopping malls and other public places will reveal the potential of commercial WiFi's scenario application without a doubt
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-cost, low-power, wireless mesh networking standard for battery-powered devices in wireless control and monitoring applications.Zigbee provides low-latency communications.Zigbee chips are typically integrated with radios and microcontrollers.Zigbee operates in the industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) radio band: 2.4 GHz in most jurisdictions around the world;... While some devices also use 784 MHz in China, 868 MHz in Europe, and 915 MHz in the United States and Australia, even these jurisdictions still use 2.4 GHz for most commercial Zigbee devices. Data rates range from 20 kbit/s (868 MHz band) to 250 kbit/s (2.4 GHz band).

Zigbee AllianceThis has now been modified to become the CSA (Connectivity Standards Alliance); with a total membership of over 500 global companies. All relevant specifications are developed and published by this organization.
Zigbee is a specification based on IEEE 802.15.4 for a set of advanced communication protocols, a low power consumption, low data rate and proximity (i.e., personal area) wireless self-organizing network is a low-speed, short-range transmission of wireless communication protocols, as a high-reliability wireless digital transmission network, the main features of the low-speed, low-power, low-cost, support for a large number of online nodes, support for a variety of online topology, low complexity, fast, reliable and secure. It is mainly suitable for use in the field of automatic control and remote control, and can be embedded in various devices.
The Zigbee protocol is suitable for embedded applications that require low power consumption and tolerance of low data rates. The resulting network will use very little power - individual devices must have a battery life of at least two years to be certified. Typical applications include home automation, wireless sensor networks, industrial control systems, medical data collection, smoke and intrusion warnings, building automation, remote wireless microphone configuration, indoor localization, and more.
UWB
Ultra Wide Band (UWB, ultra-wide band or ultraband) is a technology for transmitting information over a wide bandwidth (>500 MHz). This allows the transmission of large amounts of signal energy without interfering with conventional narrowband and carrier transmissions in the same frequency band. Regulatory restrictions in many countries allow for efficient use of radio bandwidth and enable high data rate Personal Area Network (PAN) wireless connectivity, remote low data rate applications, and radar and imaging systems that coexist transparently with existing communication systems.2019 Apple phones still apply this same technology to their phones.
Ultrawideband was previously known as pulse radio, but the FCC and the International Telecommunication Union's Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) now define UWB as antenna transmissions that transmit signals with a bandwidth greater than 500 MHz or an arithmetic center frequency of 20%, whichever is less. Thus, pulse-based systems-where each transmitted pulse occupies the UWB bandwidth (or a collection of narrowband carriers of at least 500 MHz; e.g., Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM))-can access the UWB spectrum according to rules.

The FiRa Alliance was formed in August 2019 toDevelopment of interoperable UWB ecosystems including cell phones
UWB: It does not use sinusoidal carrier, but uses nanosecond non-sinusoidal narrow pulse to transmit data, so it occupies a wide range of spectrum.UWB technology has the advantages of low system complexity, low power spectral density of the transmitted signal, insensitive to channel fading, low interception capability, high positioning accuracy, etc., especially suitable for indoor and other dense multi-path places of high-speed wireless access; the application of UWB technology can realize the safety of The application of UWB technology can realize safe ranging and accurate sensing, and create spatial environment perception for wireless devices. Application areas: radar, real-time positioning, mobile phone/smart wear/label, automotive, smart home (access control, video transmission (spatial delivery), etc. APPLE in the recent generations of cell phones are equipped with a chip that supports UWB, which makes the market for UWB become more expectable!
UWB chips are only available from a small number of suppliers; Apple, Samsung and Xiaomi have all launched UWB-enabled phones or watch products
| provider | Product Model | (an official) standard | (radio) band | Release Date |
| Microchip | ATA8350 | LRP | 6.2-7.8 GHz | Feb 2021 |
| Microchip | ATA8352 | LRP | 6.2-8.3GHz | Feb 2021 |
| NXP | NCJ29D5 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Nov 12, 2019 |
| NXP | SR100T | HRP | 6-9 GHz | Sept 17, 2019 |
| Apple Inc. | U1 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Sept 11, 2019 |
| Qorvo | DW1000 | HRP | 3.5-6.5 GHz | Nov 7, 2013 |
| Qorvo | DW3000 | HRP | 6-8.5 GHz | Jan 2019 |
| 3 dB | 3DB6830 | LRP | 6-8 GHz | |
| CEVA | RivieraWaves UWB | HRP | 3.1-10.6 GHz depending on radio | Jun 24, 2021 |
bluetooth
BLUETOOTHBluetooth: is a short-range wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances between fixed and mobile devices using UHF radio waves in the ISM band (from 2.402 GHz to 2.48 GHz) and for building personal area networks (PANs). It is primarily used as an alternative to wired connections, exchanging files between nearby portable devices and connecting cell phones and music players using wireless headsets. In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limited to 2.5 milliwatts, giving it a very short range of up to 10 meters (33 feet).

Bluetooth is a radio technology that supports short-range communication (generally within 10m) between devices, enabling wireless information exchange between many devices, including cell phones, PDAs, wireless headsets, laptop computers, and related peripherals. Utilizing Bluetooth technology can effectively simplify the communication between mobile communication terminals and devices, and can also successfully simplify the communication between devices and the Internet, so that data transmission becomes more rapid and efficient. Many devices can be set up conveniently and quickly via Bluetooth.
Bluetooth is managed by the SIG (Bluetooth Special Interest Group), more than 35,000 member companies, involving communications, computers, networking and consumer markets, so its application areas are very broad, in 2020, it is estimated that there are more than 4 billion units of Bluetooth products, is still 15% annual rate of increase.
Quuppa, the brand we represent, also achieves good results with Bluetooth technology for precise positioning.
RFID
RFID: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is an acronym for Radio Frequency Identification. The principle of non-contact data communication between the reader and the tag to achieve the purpose of identifying the target. The complete RFID system by the radio receiver read-write (Reader), radio transmitter electronic tags (Tag) and data management system consists of three parts; its principle of operation is the reader (Reader) to launch a specific frequency of radio wave energy to drive the circuit will be sent out of the internal data, at which time the Reader will be in order to receive the interpretation of the data sent to the application program to do the appropriate Processing. Passive tags are powered by the RFID reader asking for radio wave energy. Active tags are powered by batteries, so they can be read from RFID readers to read a greater range, up to several hundred meters. Unlike bar codes, the tag does not need to be in the reader's line of sight, so it may be embedded in the object being tracked.RFID is a method of Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC)

| (radio) band | realm | speed | application scenario |
| LF: 120-150 kHz | 10 cm | lower (one's head) | Animal identification, plant data collection |
| HF: 13.56 MHz | 0.1-1 m | low to medium | smart card Memory cards that do not comply with the ISO standard (Mifare Classic, etc.), ISO-compatible microprocessor cards (Desfire EV1, Seos) |
| UHF: 433 MHz | 1-100 m | center | Defense application, underground miner tracking with active tags |
| UHF: 865-868 MHz (Europe) 902-928 MHz (North America) | 1-12 m | middle to high | EAN, various standards; railroad use |
| microwave: 2450-5800 MHz | 1-2 m | your (honorific) | 802.11 wireless LAN, Bluetooth standard |
| microwave: 3.1-10 GHz | to 200 m | your (honorific) | Requires semi-active or active labels |
| mm-wave: 24.125 GHz | 10-200 m | your (honorific) | Semi-passive labeling is required. Extended range using inverse backscattering methods |
RFID has a wide range of applications. Typical applications include animal chips, car chip immobilizers, access control, parking lot control, production line automation, and material management. According toIDTECHThe forecast; the market value is expected to rise from $12.08 billion in 2020 to $16.23 billion in 2029; logistics warehousing is one of the most promising application areas of RFID, UPS, DHL, Fedex and other international logistics giants are actively experimenting with RFID technology, with a view to large-scale application in the future to enhance its logistics capabilities. Can be applied to the process include: logistics process of goods tracking, automatic information collection, warehouse management applications, port applications, postal parcels, express delivery, etc.
NFC
NFC: the Chinese full name of the near field communication technology (Near Field Communication). NFC is based on contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, the use of interconnectivity technology integration evolved through the integration of inductive readers on a single chip, inductive cards and peer-to-peer communication functions combined with wireless interconnectivity technology developed to realize the communication between two electronic devices within a distance of 4 cm or less. NFC provides low-speed connectivity through simple setup and can be used to bootstrap more powerful wireless connections. Like other "proximity card" technologies, NFC communicates in one or two directions based on inductive coupling between two so-called antennas present on NFC-enabled devices, such as smartphones and printers, using 13.56 MHz in the globally available, unlicensed RF ISM band using the ISO/IEC 18000-3 aerial band. ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard, with data rates ranging from 106 to 424 kbit/s.

These standards are provided by the NFC Forum. The Forum is responsible for promoting the technology, setting standards and certifying device compliance. Secure communications can be obtained by applying encryption algorithms, as is done with credit cards, and they comply with standards that are considered personal local area networks (LANs)
NFC and Bluetooth are both relatively short communication technologies available on cell phones. nfc operates at a slower speed and has a shorter range than bluetooth, but consumes much less power and does not require pairing. nfc is faster to set up than standard bluetooth, but has a lower transfer rate than low-power bluetooth. Instead of performing a manual configuration to recognize a device when using NFC, the connection between two NFC-enabled devices is automatically established in less than 0.1 seconds.The maximum data transfer rate of NFC (424 kbit/s) is slower than Bluetooth V2.1 (2.1 Mbit/s). It is a very safe and fast way of communication that is becoming more and more popular in our daily life.The "near field" in the Chinese name of NFC refers to the radio waves near the electromagnetic field. Application Scenario: Used in access control, time and attendance, visitor, conference sign-in, patrol, etc. NFC has the function of human-computer interaction, machine-to-machine interaction and so on.
Category IV: Wireline communications
USB
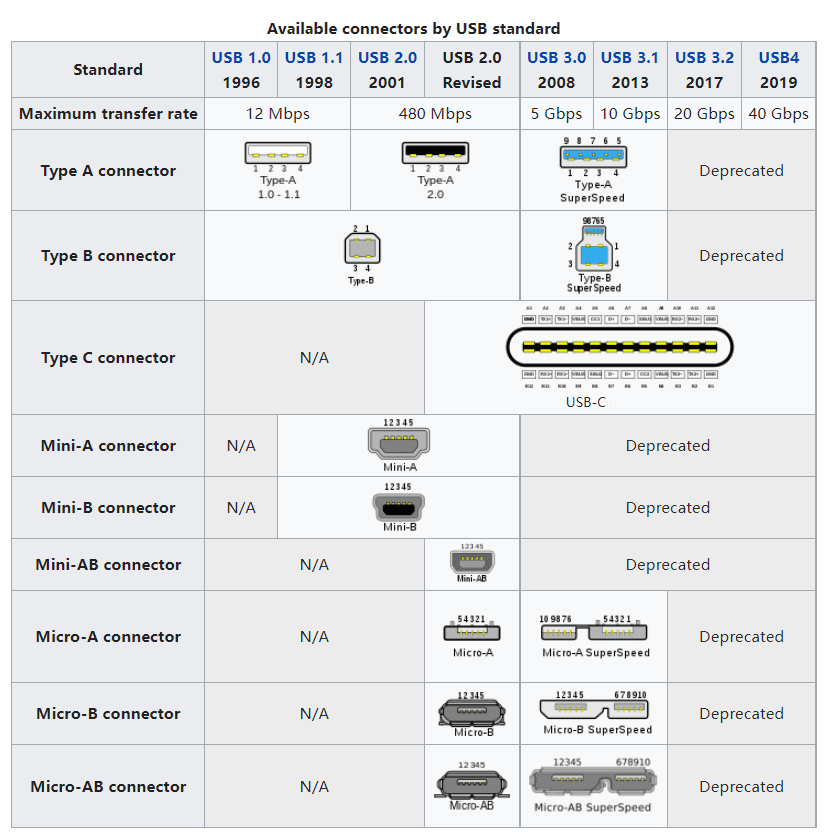
As a high-speed serial bus, USB bus can meet the requirements of high-speed data transmission environment with its extremely high transmission speed, and the bus also has the advantages of simple power supply (bus-powered), easy to install and configure (support for plug-and-play and hot-plugging), easy to expand the port (up to 127 peripherals can be expanded through the hub), diverse transmission methods (four transmission modes), and good compatibility (backward compatible after product upgrades). The bus also has the advantages of simple power supply (bus-powered), easy installation and configuration (plug-and-play and hot-plug support), easy port expansion (up to 127 peripherals via hubs), a wide variety of transmission modes (four transmission modes), and good compatibility (backward-compatible with upgrades). It is an interface technology mainly used in the PC field. It is widely used in information and communication products such as personal computers and mobile devices, as well as in other related fields such as photographic equipment, digital TV (set-top boxes), and game consoles.
USB is intended to standardize the connection of peripheral devices to personal computers in order to communicate with them and provide power. It has largely replaced interfaces such as serial and parallel ports and has become commonplace in a wide variety of devices. Examples of peripheral devices connected via USB include computer keyboards and mice, camcorders, printers, portable media players, mobile (portable) digital phones, disk drives and network adapters.
serial port communication(Serial port)
A serial port is aserial communications interface, through which information is passed in or out sequentially, one bit at a time. This is the opposite of a parallel port, which communicates with multiple bits in parallel at the same time. For most of the history of the personal computer, data has been transmitted through serial ports to devices such as modems, terminals, various peripherals, and directly between computers.
While interfaces such as Ethernet, FireWire, and USB also send data in serial streams, the term "serial port" usually indicates that the hardware complies with the requirements of the RS-232 or related standards such as RS-485 maybe RS-422
Although bit-byte (byte) serial communication is slow, a serial port can send data using one wire while receiving data using another wire. Serial communication protocol refers to the specification of the content of the data packet, which contains the start bit, body data, check bit and stop bit, and the two sides need to agree on a consistent data packet format in order to send and receive data properly. In serial communication, the commonly used protocols include RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485; the most important parameters of serial communication are baud rate, data bits, stop bits and parity. Most computers contain two RS-232 serial ports. Serial communication is also a commonly used communication protocol for instrumentation equipment.
Ethernet
Ethernet ((Ethernet)is a family of wired computer networking technologies typically used in local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs) and wide area networks (WANs). The original 10BASE5 Ethernet used coaxial cable as the shared medium, while newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data rates have increased from the original 2.94 Mbit/s [2] to the latest 400 Gbit/s, with rates as high as 1.6 Tbit/s. Ethernet standards include several cabling and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer
Ethernet is widely used in homes and industry and interoperates well with wireless Wi-Fi technology. Internet protocols are often transmitted over Ethernet, so it is also considered one of the key technologies that make up the Internet.The IEEE organization's IEEE 802.3 standard sets the technical standards for Ethernet, which specifies the content of the protocols that include the physical layer of connectivity, electronic signals, and the media access layer; industrial and automotive Ethernet applications are becoming more and more popular.
Mbus
Meter bus (meter bus, MBus) is a new type of European bus structure, has been set as the industry standard by the Ministry of Housing and Construction, MBus is mainly characterized by two non-polar transmission lines to simultaneously supply and transmit serial data, and the various sub-stations (confirmed by a different ID) in parallel in the MBus bus; MBus is used for various types of meters or related devices in the class of energy consumption intelligent When MBus is used in the intelligent management system of energy consumption of various meters or related devices, relevant data or signals can be collected and transmitted to the concentrator, and then to the master station through the corresponding interface.
The M-Bus has been developed to meet the need for networking and remote meter reading systems for utility meters, for example to measure the consumption of gas or water in the home. The bus meets the special requirements of remote-powered or battery-operated systems, including consumer utility meters. When interrogated, the meters transmit the data they collect to a common master, such as a handheld computer, which is periodically connected to read all of the building's utility meters. An alternative method of centralized data collection is to transmit meter readings via modem.
Other applications for which M-Bus is suitable, such as alarm systems, flexible lighting fixtures, heating control, etc.
Content review.





