Internet of Things (IoT)Sensing and control systemsSolenoid valves are one of the most complex technologies used in industrial applications, and they consist of complex components that work in tandem to control the flow of liquids and gases, making them critical to a variety of processes. In this article, we will explore how solenoid valves work, their key components, and the various types available on the market today. We will also discuss some of the applications where solenoid valves can be used, as well as some tips on how to maintain them. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of why solenoid valves are so important to industries around the world.
How do solenoid valves work?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluids. The most common types of solenoid valves are two-way or three-way valves that consist of a coil and a movable armature. When the coil is energized, the armature is pulled toward the coil to open or close the valve.
Solenoid valves are used in a variety of applications, such as controlling the flow of water in sprinkler systems or regulating air pressure in automobile tires. The key components of a solenoid valve are the coil, armature and seat. When the coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that draws the armature to it. This pushes the seat against the opening or closing spring, which opens or closes the valve.
Solenoid valves can be used to control the on/off and regulation functions in a system. They are relatively simple and inexpensive devices that can be used to control many types of fluids, such as water, air, and steam.
Solenoid valves can be normally open or normally closed. In a normally open solenoid valve, the valve opens when the power is off and closes when the power is on. In a normally closed solenoid valve, the valve closes when the power is off and opens when the power is on.

When an electric current passes through a coil, an electromagnetic field is created. This magnetic field attracts the plunger and moves it in an upward direction. This opens the orifice of the valve and allows the medium to flow through the valve
Solenoid Valve Type
Solenoid valves are used in a variety of industries and applications. Different types of solenoid valves include:
- Direct Acting Solenoid Valve: This type of valve is the most common type of solenoid valve. It consists of a coil that surrounds a plunger. When the coil is energized, the plunger is pulled into the coil, which opens the valve.
- Pilot Operated Diaphragm Solenoid Valves: This type of valve uses a pilot signal to open or close the valve. The pilot signal is used to move the diaphragm, which opens or closes the valve.
- Pilot Operated Check Valve: This type of check valve has a check ball located on top of the plunger. When the coil is energized, the plunger opens the check ball allowing flow through the valve.
The most common type of solenoid valve is the two-way solenoid valve. A two-way solenoid valve has two ports and two positions: one position for opening the valve and one position for closing the valve. Three-way solenoid valves have three ports and three positions: one position for opening the valve, one position for closing the valve, and one position for bypassing the valve.
Solenoid valves are available in a variety of materials, including brass, stainless steel and plastic. The material you choose will depend on the application and operating conditions.
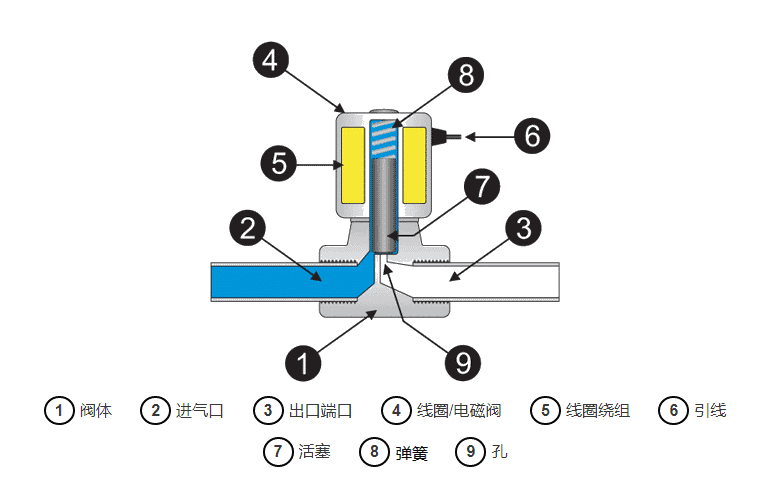
The diagram at right depicts the basic components of a solenoid valve. The valve shown in the diagram is a normally closed direct acting valve. This type of solenoid valve has the simplest and easiest to understand principle of operation.
Solenoid valve selection criteria
- Type of solenoid valve: This depends on whether your application requires a 2-way or 3-way solenoid valve.
- Housing material: This depends on the medium in which the valve is used. We need to check the chemical properties and temperature of the medium. Usually, brass is used. Stainless steel has good chemical resistance, temperature resistance and pressure resistance.
- Seal Material: Seal material should be selected based on the chemical properties and temperature of the medium. nBR, EPDM, FKM (Viton) and PTFE (Teflon) are common choices.
- OPERATING VOLTAGE: The solenoid valves are available in AC and DC operating voltages. Choose according to your supply availability.
- Valve Function: Normally open or normally closed can be selected depending on your application. The most commonly used solenoid valve is the normally open type.
- Type of operation: There are direct-acting, indirect-acting and semi-direct-acting valves.
- Temperature: The valve material should withstand minimum and maximum temperatures regardless of where it is installed.
- Response Time: Response time is the time it takes for a valve to move from the open to closed or closed to open position. Direct acting solenoid valves are much faster than indirect acting or semi-direct acting solenoid valves.
Solenoid Valve Applications
Solenoid valves are used in a wide variety of industries and applications. Here are a few examples of solenoid valves you may find at work:
- Automotive industry: fuel injectors, transmissions transmissions
- HVAC industry: air conditioning, refrigeration systems
- Medical industry: blood pressure monitors, dialysis machines
- Food and beverage industry: coffee machines, soda dispensers
- Water treatment industry: reverse osmosis system, chemical dosing system
- Plumbing industry: shower valves, faucets, water softeners
Major suppliers
Major producers include:Emerson (name), Rotork (name) ,struggle for mastery,Siemens (company name), AUMA, Honeywell (name),Johnson Controls ,Schneider (name),Samson (name),Azibel (name),Danvers (name),Neles,Neptronic,KMC Controls,Dwyer (name),Kennault, capital of Uganda, Shenzhen Winson Automation,Nippon Gear
Content review.





